Every cloud database requires robust security features to protect the data within it from theft, unauthorized access, and leaks. Data encryption must protect data both at rest and in transit. Strong access controls help ensure that sensitive data and private information is protected from unauthorized access. Data redaction capabilities ensure that visibility is strictly limited and controlled. A multilayered approach to enterprise cloud security can help to prevent breaches.
An introduction to cloud databases
As the volume of data within enterprise databases continues to grow exponentially, more organizations are turning to cloud database technology to reduce costs, increase scalability, and enhance database performance. Here’s a brief introduction to how cloud databases work and how organizations may benefit from them.
What are cloud databases?
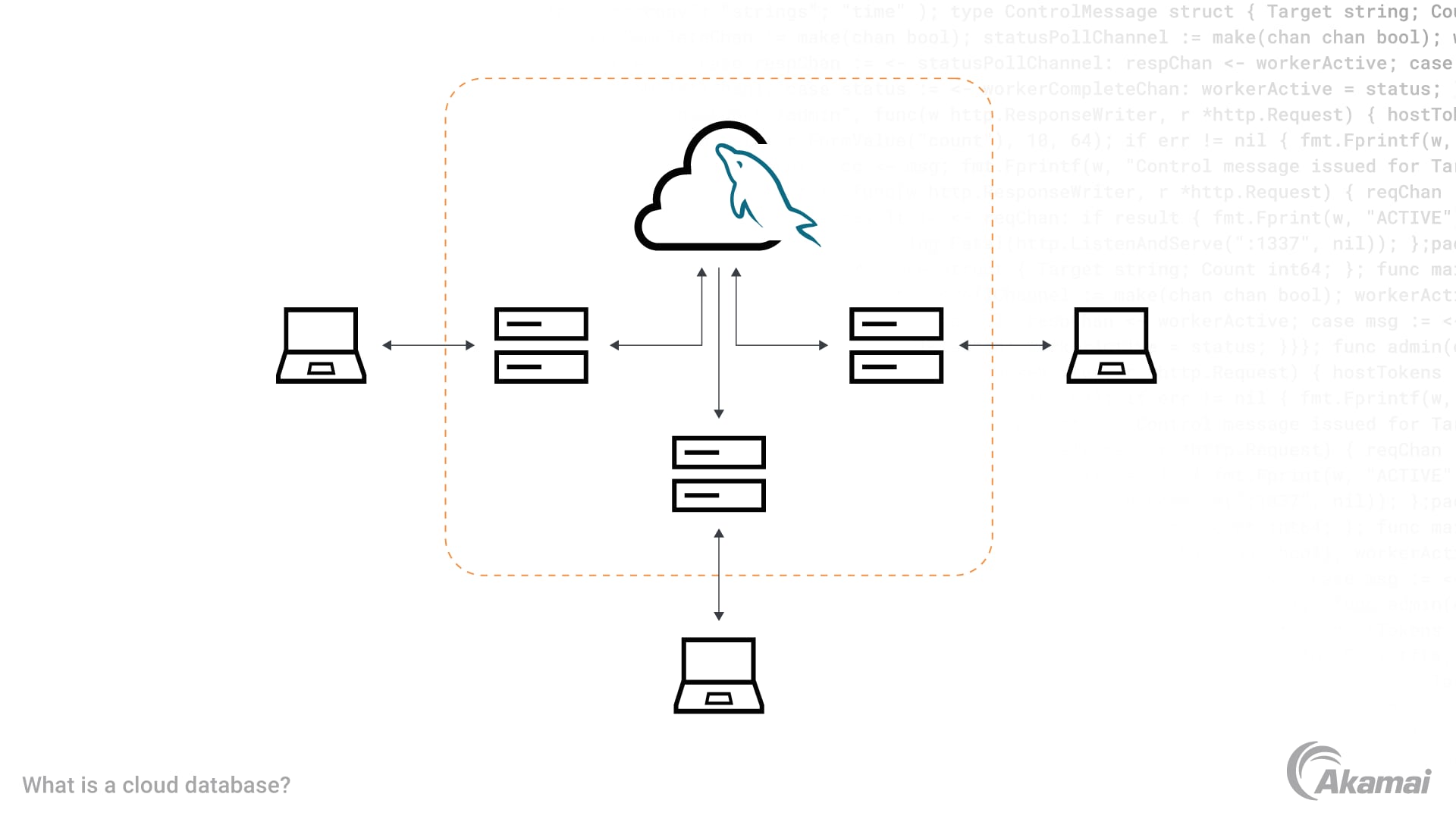 Diagram illustrates clients accessing a MySQL database via virtual machines deployed in the cloud.
Diagram illustrates clients accessing a MySQL database via virtual machines deployed in the cloud.
Cloud databases are database services that are accessed via a cloud platform on the internet. These databases have the same features and serve the same functions as a traditional database on in-house servers, but they provide the added flexibility of cloud computing: speed, agility, scalability, and lower costs. To users or applications, the information and interactions with a database in the cloud will seem identical to an on-premises database. Cloud databases are designed to run in public cloud or hybrid cloud environments.
What are the benefits of cloud databases?
Cloud databases offer a wide range of advantages over traditional, on-premises solutions.
- Enhanced accessibility. While traditional databases must be accessed via a corporate network, cloud databases can be accessed from any location on a variety of internet-connected devices.
- Improved agility. Resources can be provisioned or taken offline in minutes, making it easy to quickly test, validate, and operationalize new business ideas.
- Easier scalability. Databases in the cloud can scale up and down quickly and cost-efficiently as business requirements change.
- Greater reliability. Cloud database platforms typically offer a variety of features, such as automatic failover and autoscaling, that are designed to ensure high availability.
- Lower TCO. A pay-as-you-go model for consuming database resources in the cloud enables organizations to reduce the total cost of ownership.
- Reduced costs. Cloud databases reduce costs by eliminating the need to manage and maintain physical infrastructure. IT teams can rely on cloud providers to provision, update, and maintain all the hardware, software, and operating systems for a database in the cloud.
- Faster recovery. By enabling automated, secure backups on remote servers, cloud databases improve recovery after a natural disaster, power outage, or equipment failure.
- Strong security. Cloud database providers typically offer multiple layers of security and enable enforcement of centralized security policies.
- Expert support. Cloud database providers may offer greater expertise in managing and supporting a database than the skills available within an in-house IT staff.
- Less risk. Cloud database providers can automatically enforce security best practices to reduce the probability of user error. High-availability features and service-level agreements (SLAs) can eliminate loss of revenue due to downtime.
What are cloud database deployment models?
Organizations may access cloud databases in several deployment models.
- Self-managed. With a self-managed option, an organization and its administrators and developers are responsible for managing the database, including purchasing instances and running databases on virtual machines.
- Automated. In this model, organizations use cloud service APIs to assist with operations while maintaining access to and control of database servers and operating systems.
- Managed services. In a fully managed model, a cloud service provider is responsible for provisioning, scaling, monitoring, backing up, and securing the database.
- Autonomous. In this model, automation and machine learning technology handle database management and performance tuning, eliminating the need for human intervention. Autonomous databases automate security, backups, updates, and other routine management tasks.
What is a cloud database as a service (DBaaS)?
The database as a service (DBaaS) model, also known as a fully managed model, enables companies to take advantage of the benefits of a cloud database without needing to purchase, install, configure, maintain, and upgrade hardware or software. Database services are provided by a cloud service provider, which handles data management, administration, maintenance, and operational tasks.
Benefits of DBaaS offerings include:
Ease of management. IT and development teams and database administrators can leave database management to a DBaaS vendor, freeing them to focus on applications and development.
Expert support. Cloud DBaaS providers can offer the support of database experts 24/7.
Fast implementation. DBaaS services enable companies to deploy cloud infrastructure for databases quickly, without needing to add staff or invest in hardware and software.
Easy scaling. Organizations can quickly scale their cloud databases up or down as needed to meet business requirements.
No capital investment. DBaaS services may be purchased as operational expenses with a predictable monthly expense, eliminating the need for capital investment.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cloud databases are available in two general categories: Structured Query Language (SQL) relational databases and NoSQL non-relational databases. SQL databases enable users and applications to quickly access, query, and write to the database, and nearly every function can be accomplished in the SQL programming language. NoSQL databases can store both structured and unstructured data, handling enormous volumes of data at superfast speeds.
Many of the world’s largest enterprises rely on cloud databases to ensure that their information is easily accessible, highly secure, and continuously backed up. Many consumers also use databases in the cloud as part of publicly available software as a service (SaaS)-based apps.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.

