Threats to DNS servers are any type of attack that compromises the availability, speed, and performance of DNS services. These include DNS floods that overwhelm DNS servers with requests for resources, rendering servers unavailable for legitimate requests. DNS spoofing or cache poisoning is a type of cyberattack that redirects traffic to a fraudulent website. DNS tunneling uses data encoded in DNS queries and responses to hijack a DNS server and enable attackers to manage it remotely.
Ensure availability and security of your DNS servers
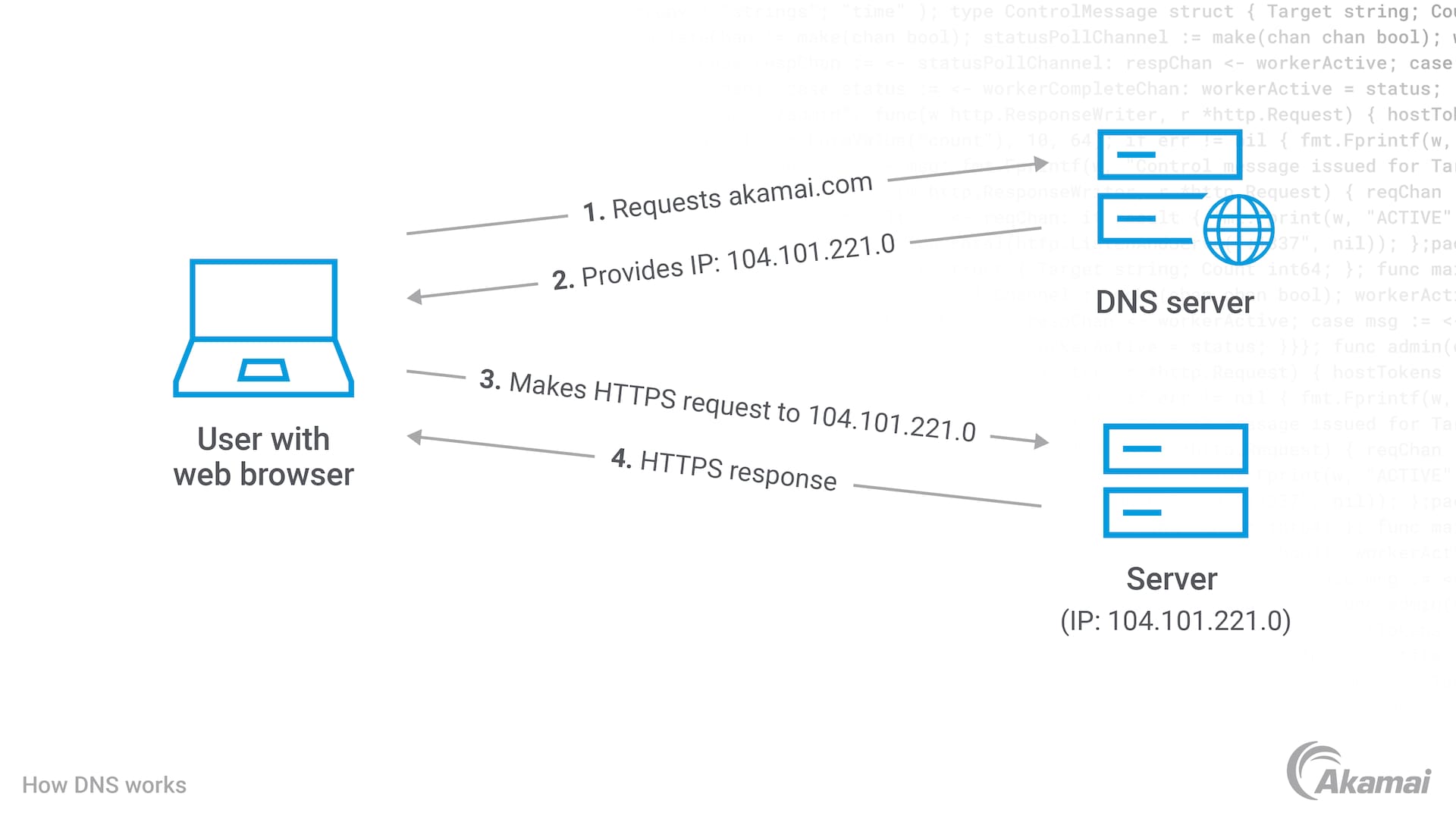
Domain Name System (DNS) servers translate the readable domain hostnames used by humans — such as www.companywebsite.com — into IP addresses that can be read by machines. DNS servers are essential to ensuring a positive browsing experience as well as fast and reliable internet connections to websites, APIs, and enterprise application software hosted in the cloud.
Protecting DNS servers is a business-critical priority for your IT security teams. Because DNS enables your users to access web applications and APIs, any threat to your DNS servers is also a threat to business operations, profitability, and trust with customers and partners.
Despite the criticality of DNS resolution for website and application performance, many organizations have not invested in adequate DNS infrastructure, often relying on just two or three DNS servers to connect users with the websites and applications they’re seeking. This approach leaves DNS services vulnerable to distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks as well as data center outages.
Akamai Edge DNS is a cloud-based solution that delivers 24/7 availability, enhances responsiveness, and improves the resilience of DNS servers as they defend against the largest DDoS attacks.
Akamai Edge DNS
Akamai originally built Edge DNS to deliver authoritative DNS services to support solutions on our global content delivery network (CDN). With our massively distributed edge and cloud platform, we have architected Edge DNS for greater scale than most competing authoritative DNS services on the market today. While competing DNS servers and solutions are typically focused solely on performance, Edge DNS is designed to deliver high availability and greater resiliency against attacks in addition to exceptional performance.
Edge DNS employs an IP anycast model to respond to DNS queries. This means that rather than relying on two or three DNS servers, Akamai customers can access thousands of nameservers deployed in more than 4,100 points of presence worldwide. IP anycast directs queries from end users to the closest point of presence for resolution, enabling faster performance, greater scale, and more diverse distribution. While leveraging IP anycast is not unique to Akamai, we also segment nameservers and points of presence into multiple IP anycast clouds, making Edge DNS equivalent to multiple standalone DNS providers in terms of availability, scale, and distribution.
With Akamai Edge DNS servers, you can:
- Rely on guaranteed, nonstop DNS availability. A 100% uptime SLA and resilient architecture deliver mission-critical DNS services.
- Manage DNS cost. Predictable, zone-based billing lets you avoid unexpected charges from high DNS usage.
- Ensure access with secondary DNS servers. Augment your primary DNS server availability through the use of internet-facing secondary zones with Edge DNS.
Edge DNS is part of a suite of application and API security solutions that enable organizations to defend against a wide range of multi-vector attacks. Akamai App & API Protector provides one-stop app security with defenses against web application and API attacks. Prolexic offers the most effective defense for stopping DDoS attacks at scale. And Client-side Protection & Compliance defends sites from client-side threats by spotting and blocking malicious activity.
Domain monitoring and takedown
In addition to DNS redundancy for your domains, domain security also requires monitoring the internet for look-alike names, and disrupting usage of names that impact the brand negatively with fake websites that spoof brands and steal traffic and personal information such as user credentials. With Zone Protection and domain Takedown, you can proactively learn of third-party domains with bad intentions and disrupt usage on the internet. For each domain with monitoring, a list of related domains will be available with a set of attributes such as its risk level. For each, a set of actions is available, including: [a] follow a domain for changes, e.g., new MX (mail exchange) records, [b] tag a domain for tracking, [c] set a priority for sorting, and [d] takedown.
Advantages of Edge DNS
Guarantee 24/7 availability for DNS servers. By leveraging Akamai’s scalable, globally distributed platform, you can ensure that your customers, employees, and partners can quickly access your web applications and APIs.
Block the largest DDoS attacks. The unparalleled scale and capacity of Akamai Connected Cloud ensures that Edge DNS can absorb the largest DDoS attacks while still providing access to users. Built-in resiliency controls enable availability durable against wide ranges of DNS attack types.
Ensure faster, more reliable resolution. Zone apex mapping and thousands of DNS servers worldwide deliver reliable, fast DNS performance.
Manage costs more easily. With pricing based on the number of zones rather than the number of requests, you can control your DNS cost with greater precision.
Prevent DNS forgery. Block attacks caused by DNS forgery with Domain Name System Security Extensions (DNSSEC).
Simplify management. Akamai Control Center, Edge DNS APIs, and integration such as Terraform streamline management of DNS infrastructure.
Manage DNS as code. Allow developers to use APIs and existing management tools to automate Edge DNS workflow.
Domain monitoring and takedown. Track the internet for look-alike domain names and disrupt domains that are spoofing and infringing on your brand.
DDoS controls with Edge DNS
While the architectural design, scale, and capacity of Edge DNS delivers greater resiliency during DDoS attacks, our DNS servers also offer security controls that can help to mitigate the impact of a DNS flood, a specific type of DDoS attack. DNS floods use enormous volumes of legitimate DNS requests to consume an overwhelming amount of compute and memory resources on physical nameservers. As a result, these targeted DNS servers cannot respond to queries from legitimate end users.
To defend against DNS floods, Edge DNS provides several essential capabilities:
- The ability to scale. The scale of our authoritative DNS servers is up to several times that of competitors’ solutions. Using thousands of nameservers deployed in more than 1,000 points of presence around the world, Edge DNS delivers compute and memory resources to sufficiently absorb large spikes in requests from DNS floods.
- Rate limiting. Edge DNS settings can be configured to automatically drop requests from suspect resolvers after the number of requests surpasses a defined threshold. Rate limiting prevents spikes in DNS requests from overconsuming compute memory resources, which can be helpful when handling attacks that generate a large volume of requests while consuming relatively low bandwidth.
- DNS allowlisting. The unparalleled scale and capacity of Akamai Intelligent Connected Cloud provides our threat researchers with unique visibility into the behavior of recursive resolvers that are responsible for roughly 95% of legitimate DNS lookups. When necessary, Edge DNS can deploy a positive security model to restrict activity to a group of DNS resolvers that are known to be good.
Global Traffic Management
When combined with Edge DNS, Global Traffic Management (GTM) provides a complete set of DNS controls, such as geographically mapping users to resources in specific regions of the world or distributing traffic evenly across multiple geographic locations and with a preference for each user to utilize a geographically close edge server.
GTM is a DNS-based cloud-based server load balancer that leverages the intelligence and scale of Akamai Connected Cloud to provide fault tolerance, high performance, and non-stop availability for web and API traffic. Using a broad set of rules and variables, GTM uses standard DNS workflow to route end-user requests to the data center best able to optimally deliver content to that user. And because Akamai Connected Cloud is a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, GTM is better able to accomplish its role than any comparable service. Used by some of the world’s largest and best-known enterprises spread across many industries, GTM offers a perfect combination of functionality and usability, through a combination of the Akamai Control Center, a robust API, and strong DevOps integration.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
IP anycast is a network routing technique where multiple identical network nodes are deployed across a distributed network to provide a single common IP address. All nodes respond to the same IP address, and traffic is routed to the nearest node based on routing protocols, thus providing users with the lowest latency and highest availability.
A load balancer is a device that distributes network or application traffic across a number of servers. Load balancers are used to increase capacity (concurrent users) and reliability of applications. They improve the overall performance of applications by decreasing the burden on servers associated with managing and maintaining application and network sessions, as well as by performing application-specific tasks.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.