Bot traffic simply refers to web traffic that is generated by good or bad bots. Traffic bots are bots designed to artificially create traffic on a website, to increase likes on a social media account, or to drive up non-human traffic metrics in other ways.
The rise — and the dangers — of traffic bots
Traffic bots are computer programs that can be launched on a network to artificially create traffic on websites and social media. By repeatedly visiting a website, traffic bots drive up the number of page views, potentially increasing the site’s ranking on search engines. Traffic bots on social media can drive up likes, potentially enhancing the influence of an account. Traffic bots may also be used in more illicit activities, such as repeatedly clicking on a competitor’s paid ads to drain their advertising budget.
Traffic bots are just a small portion of the types of bot traffic generating non-human visits on corporate websites. It’s estimated that up to 70% of all website traffic today comes from bots. And while technologies like chatbots or search engine crawlers perform helpful activities, a significant number of them account for malicious bot traffic.
Akamai Bot Manager provides the tools security teams need to detect and stop bot traffic or block bot activity on their websites. With this Akamai bot management solution, website owners and providers can run automated operations more effectively and safely, allowing good bot traffic while mitigating vulnerabilities and malicious activity at the edge.
How traffic bots work
A bot is a software program designed to perform a specific set of tasks. These automated applications are fast and accurate, allowing them to perform highly repetitive tasks with greater speed and precision than a human being can.
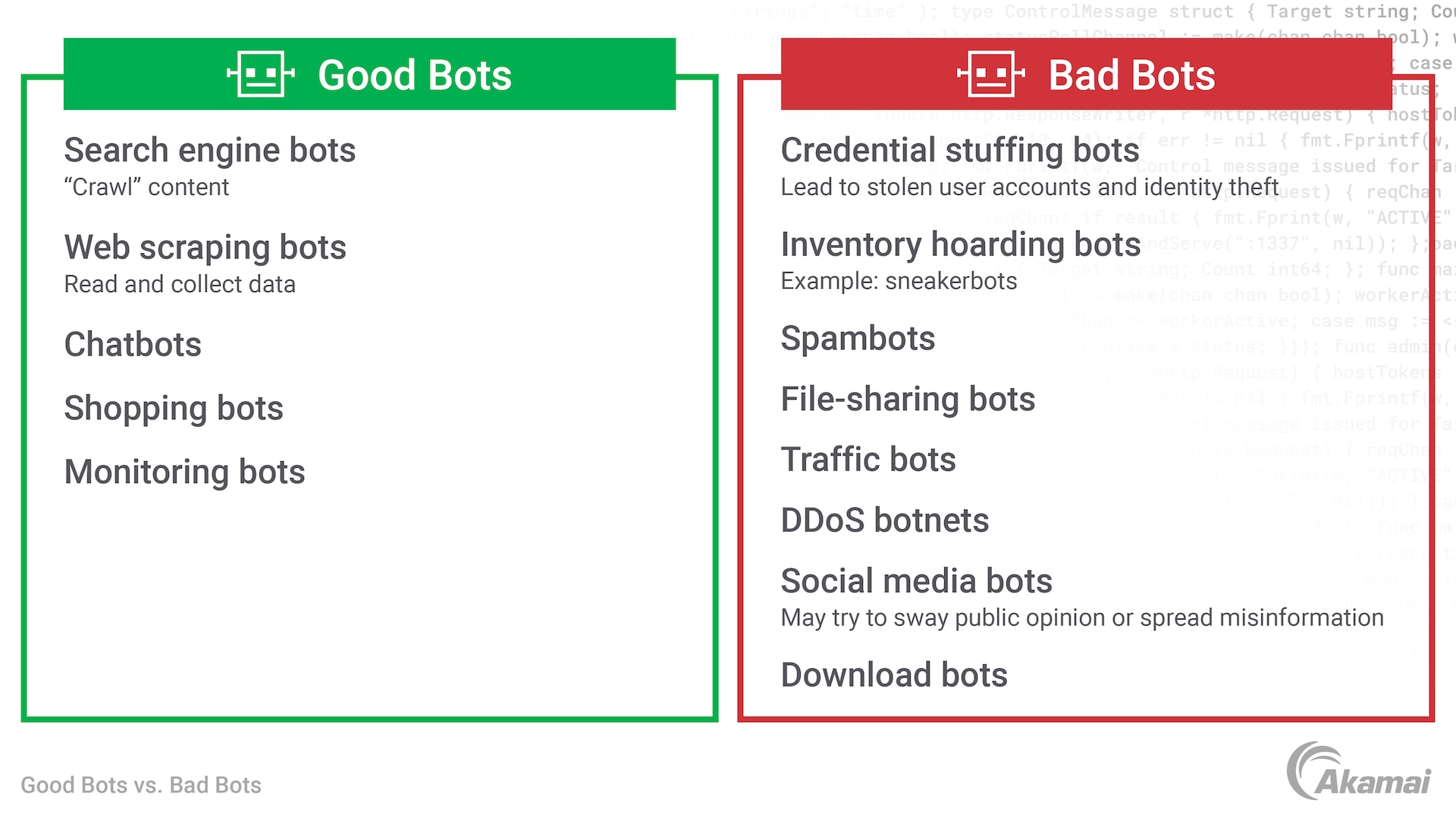
Bots are programmed to provide a wide range of activities — from knowledge bots that collect analytics data from different websites to shopping bots programmed to find the best deals from online stores. However, some bots are designed for illicit, malicious, or illegal activities. When hackers use malware to convert thousands or millions of computers and devices into bots to form a bot network or botnet, they can perform large-scale attacks like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) campaigns, credential stuffing attacks, brute-force attacks, and other devastating forms of cybercrime.
Traffic bots are a specific kind of bot, designed to emulate human activity to increase internet traffic for web pages and social media accounts. Traffic bots can also be used for click fraud or ad fraud, where bots repeatedly click on pay-per-click links to drive up revenue. While traffic bots aren’t necessarily illegal, they can increase costs, consume resources, and skew a company’s understanding of legitimate traffic.
The challenge of mitigating traffic bots or preventing malicious botnet traffic is that detection engines designed to detect bot traffic may not always distinguish good bots from malicious bots. In these cases, helpful bot traffic may be blocked, hindering productivity and compromising online experiences for legitimate users on websites. To manage and mitigate bad bot traffic without slowing down performance, security teams need sophisticated bot detection technologies that can identify malicious activity with few false positives. That’s where Akamai can help.
Manage traffic bots with Akamai
Akamai Bot Manager provides security teams with exceptional visibility and control over bots to safeguard the business and protect the trust of customers. Using multiple patented technologies, Bot Manager identifies bots where they make initial contact and mitigates bad bots before they can reach a website. To distinguish good bots from bad, Bot Manager analyzes “clean traffic” data across a wide distribution of traffic types, patterns, and volume, training the Akamai algorithms to recognize what normal traffic looks like and how good bots operate.
Using this information in combination with a variety of detection triggers, Akamai Account Protector provides a Bot Score — an accurate assessment that determines the likelihood a request is coming from a bot or a human being. Based on the Bot Score, Akamai automatically initiates a response, monitoring low-scoring requests while mitigating high-scoring requests that have definitely originated with a bot. Account Protector issues challenges for requests in the gray area in the middle, forcing bots to spend CPU cycles on minimum-time-to-solve cryptographic puzzles that slow sophisticated bot attacks to a crawl while increasing costs for attackers.
Akamai’s anti-bot technology is informed by remarkable visibility into worldwide internet conditions. When new bots are detected at one Akamai customer, the data is automatically added to a library of known bots and reflected in the detection algorithms within Bot Manager. This Akamai technology can be deployed quickly and seamlessly, and provides an accurate assessment from the moment it is turned on, detecting bots in real time with no latency or impact on user experience and network performance.
Additional bot management technology
Along with Bot Manager, Akamai delivers additional protection against botnet traffic with Account Protector. This Akamai solution delivers comprehensive protection against fraudulent human logons while mitigating the sophisticated adversarial bots that often precede attempts at account takeover.
Using behavioral detections, Account Protector profiles the typical activity patterns of account owners while also learning device anomalies and source reputation. As customer login requests are received, Account Protector determines the risk that the request is fraudulent rather than legitimate. This assessment is based on typical user behaviors such as devices used, IP addresses, networks, locations, and frequency and time of logins, among others.
Account Protector also detects and mitigates harmful bots using AI and machine learning models and techniques. These include behavior/telemetry analysis, browser fingerprinting, automated browser detection, high request rate, HTTP anomaly detection, and more.
With Akamai Bot Manager, security teams can:
Accurately recognize and allow good bots while mitigating bad bots such as traffic bots, search engine bots, spambots, and botnet traffic that may be part of a DDoS attack
Autotune bot detections based on the profiles of users and populations to increase detections while minimizing false positives
Minimize the fallout from remediation, reducing the cost and resources needed to investigate compromised accounts, replace stolen assets, and make reports to regulatory and legal authorities
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A bot is an application programmed to perform specific tasks and to run independently of human intervention. Legitimate bots perform highly useful activities. Chatbots, for example, help customers to get answers to questions or navigate a website. Web crawling bots index the content on websites for search engines. Bots may also be malicious, such as spambots that harvest email addresses from websites or bots that attempt to guess the login credentials for a user’s account.
A traffic bot is designed to artificially increase traffic metrics on a website or social media account. Traffic bots may also be used to repeatedly click on links for paid ads on a site to increase revenue for pay-for-click businesses or to drain a competitor’s advertising budget.
Yes, bot traffic can affect search engine optimization (SEO). Search engines take into account the amount of bot traffic when determining the quality of a website. If a website has a high amount of bot traffic, it could be seen as suspicious and could negatively affect the website’s ranking in search engine results.
- Monitor IP addresses: Keep an eye on the IP addresses that are making requests to your site. If you see the same IP address making multiple requests in a short period of time, it is likely to be a bot.
- Monitor user-agent strings: Most bots include a user-agent string in their requests that identifies them as a bot. By keeping track of the user-agent strings, you can identify when a bot is making a request.
- Monitor page requests: If you notice an unusually high number of requests for a particular page or set of pages, it could be a sign of bot activity.
- Track page load times: If the page load times for certain pages seem unusually fast, it could be an indication of a bot scraping your content.
- Monitor form submissions: If you are seeing a high number of form submissions with incomplete or invalid data, it could be a sign of a bot attempting to submit spam content.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.