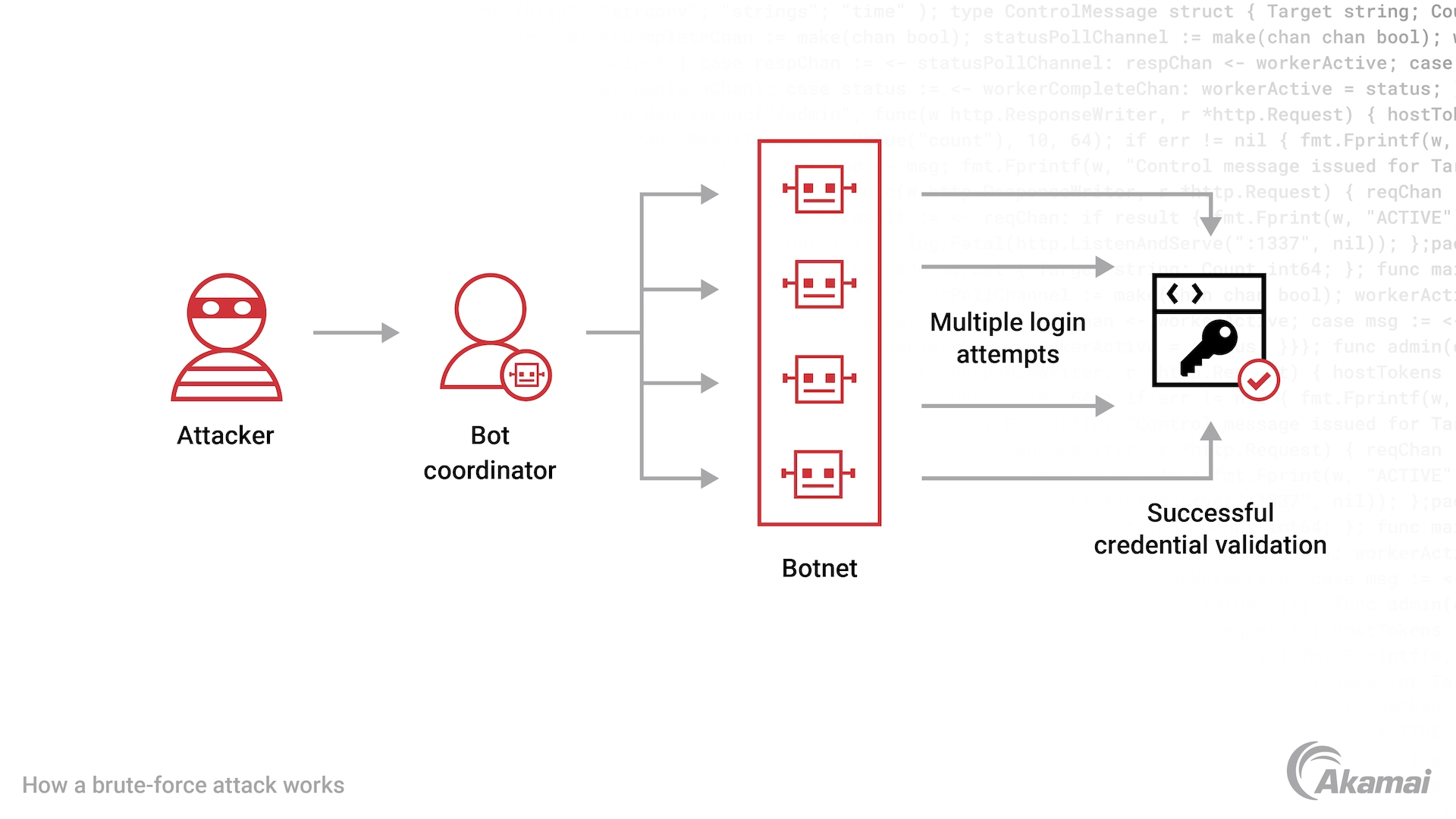
A brute-force attack is a type of cyberattack where malicious actors use botnets or automated software to guess the correct combination of usernames, passwords, and other authentication details to gain access to a system, website, or application. This type of attack is typically used by hackers to gain access to sensitive information and data.
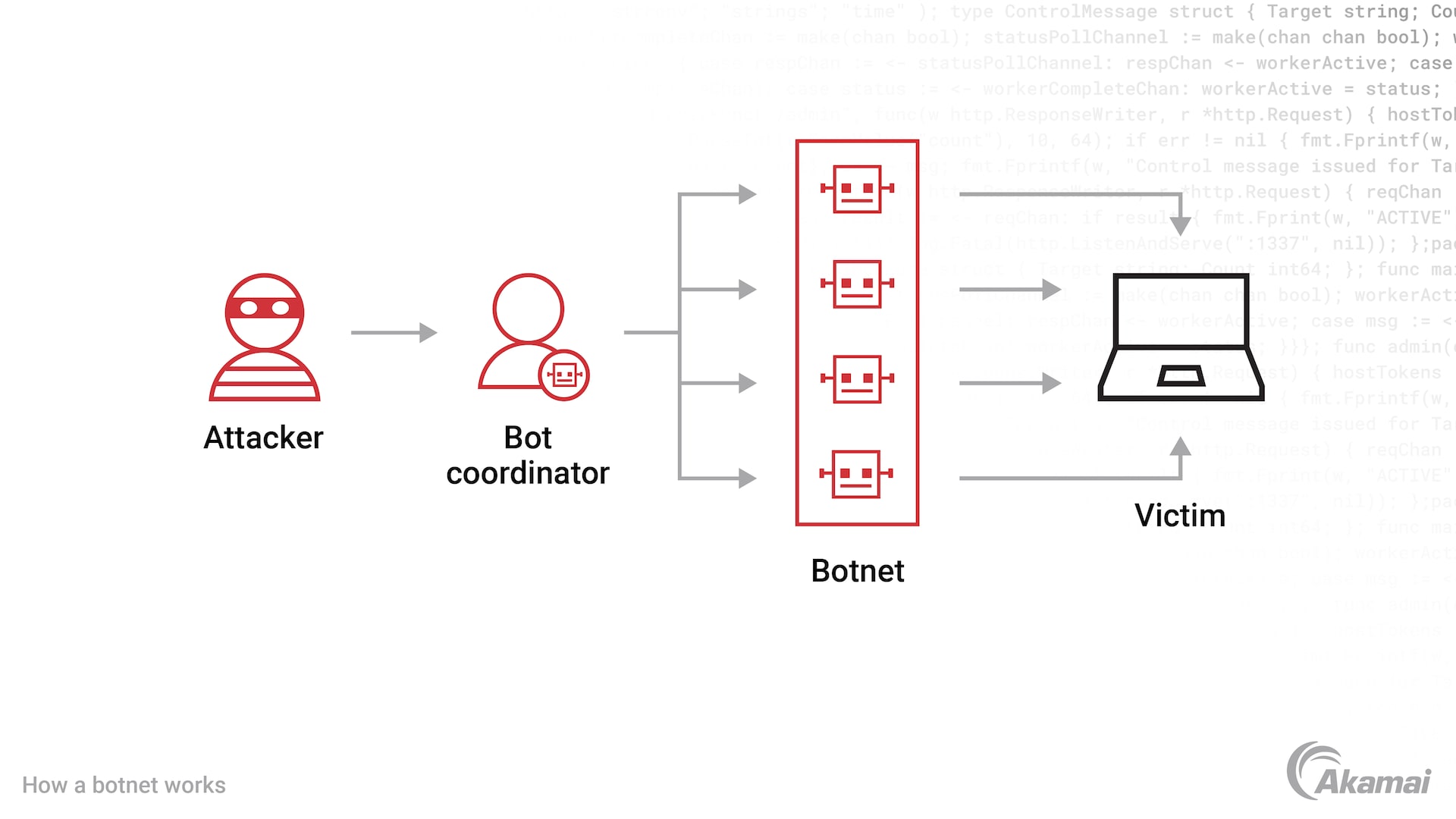
A botnet is a network of computers infected with malicious software (malware) and controlled by an attacker or cybercriminal. The computers in the botnet can be used to launch coordinated attacks such as account takeover, distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks, and phishing campaigns, and to steal sensitive information. Botnets can be used for a variety of other malicious activities as well.
The dangers of botnet traffic
Botnets continue to be a preferred tool for cybercriminals as they seek to access accounts, steal data, commit fraud, and disrupt business. By infecting thousands or millions of malware-infected computers and internet-connected devices, hackers can take control of these machines and use them to launch DDoS campaigns, send spam messages, generate fake internet traffic, and enable many other criminal and malicious acts.
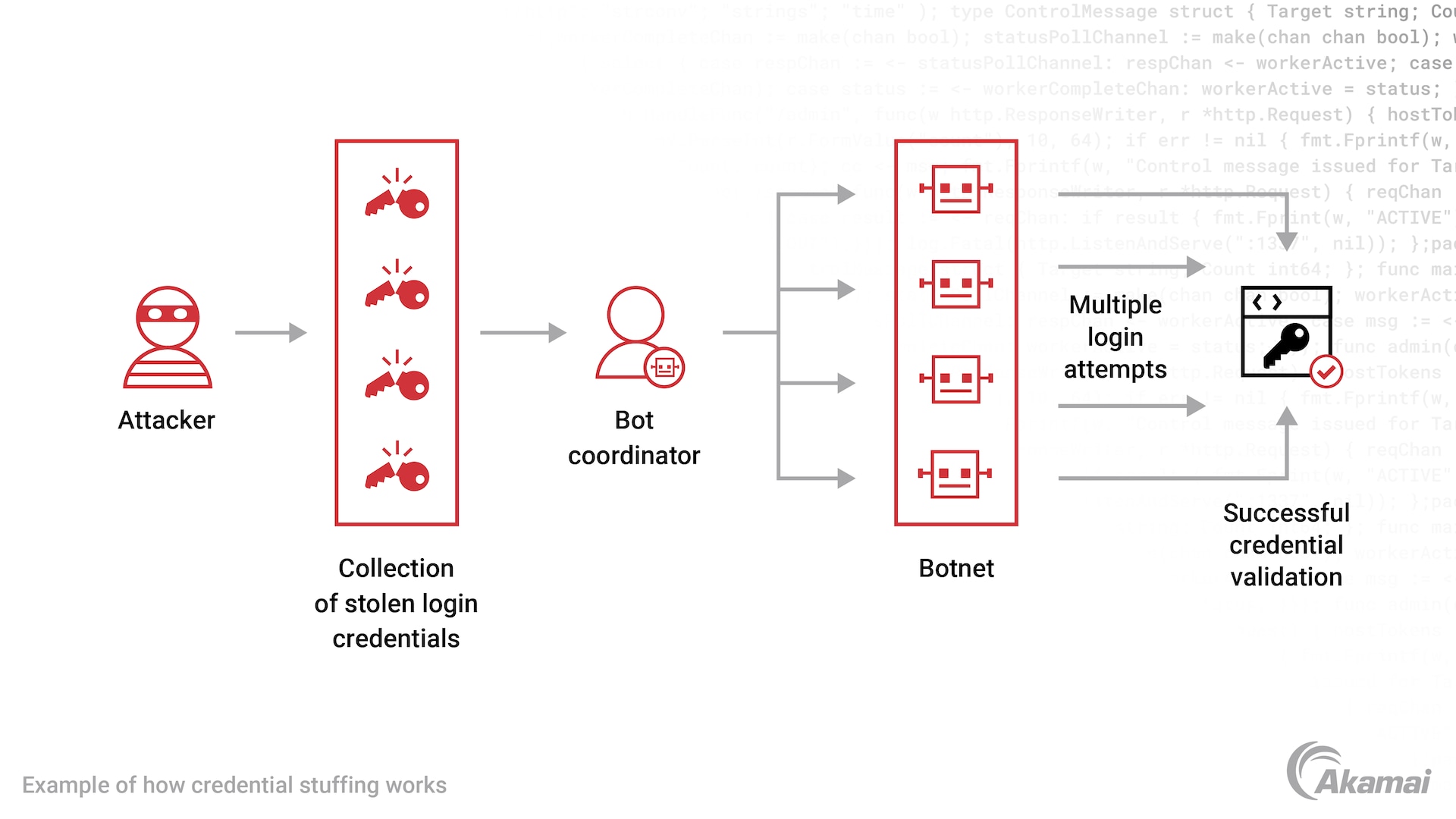
Account takeover attacks and credential stuffing are among the most dangerous uses of a botnet. Using stolen credentials purchased on the dark web, threat actors use botnets to inject username and password pairs into the login pages of a large number of websites, attempting hundreds of thousands of logins per hour. Because many individuals reuse passwords from site to site, these stolen credentials will often eventually enable attackers to gain unauthorized access to a user or business account. When credential stuffing attacks are successful, the loss of money, privacy, and trust for businesses and their customers can be devastating.
Akamai can help. Our Account Protector solution effectively stops botnet attacks, credential stuffing, and other types of attacks with smart detection and bot mitigation technologies. By identifying suspicious behavior in real time, Akamai protects online relationships and transactions without disrupting the online experience for customers.
The challenge of blocking credential stuffing with botnets
Botnets enable cybercriminals to automate their credential stuffing campaigns. By directing a botnet to continuously ping login or account pages with credentials purchased from the dark web, attackers can make hundreds of thousands of scam attempts per hour with very little effort. When a set of credentials produces a valid login on a website, attackers may sell this information to other fraudsters who use these credentials to log into sites, take over accounts and IP addresses, buy merchandise, and commit other types of fraud that deliver a hefty profit.
There are several challenges in attempting to stop botnets and credential stuffing.
Poor password hygiene. Many users repurpose the same login credentials across multiple accounts. When a data breach on one account exposes valid usernames and passwords, attackers can purchase this information from dark web sources and use it in botnet campaigns to access other accounts.
Volume of attacks. Attackers have sometimes made as many as 1 billion credential stuffing attempts in one day. Defending against this volume of cyberattacks requires a solution with massive bandwidth and scale.
Recognition difficulties. Login requests resulting from credential stuffing via a botnet typically do not have patterns that can be easily identified and blocked by threat detection solutions.
To improve bot security, many organizations invest in bot management technology designed to detect and mitigate botnets. However, bot operators have become quite sophisticated at mutating bots and botnets after initial detection to avoid recognition on subsequent attempts. That’s why a growing number of global organizations are turning to bot management technology from Akamai.
Stop botnets with Akamai Account Protector
Akamai Account Protector is a comprehensive solution designed to prevent credential stuffing and account takeover attempts, as well as the traffic from malicious software and adversarial bots that often precede these attacks.
Superior bot detection is the key to stopping traffic from bots and botnets without blocking legitimate users or slowing down performance. Account Protector accomplishes this by understanding the normal behavior of legitimate account owners and assessing the validity of each authentication request by searching for unusual behavior and anomalies. This Akamai technology applies the appropriate response to each request, taking action at the edge in real time without affecting the experience of legitimate account owners.
Account Protector defends against sophisticated botnet malware by detecting and mitigating harmful bots using AI and machine learning models and techniques. These include user behavior/telemetry analysis, automated browser detection, high request rates, HTTP anomaly detection, browser fingerprinting, and other approaches.
With Akamai Account Protector, security teams can:
- Protect the trust of customers. Understand which interactions are legitimate and which must be blocked, protecting customers from fraudulent activity while continuing to deliver exceptional functionality and online experiences.
- Tailor botnet defenses. Auto-tuning technology enables customized anomaly detection and protection, refining mitigation efforts based on the specific user population profiles of the organization.
- Gain greater insight and visibility. Security and fraud teams can take nuanced action based on transparent signals and indicators, rather than relying on yes/no types of analyses.
- Minimize fallout from remediation. With Akamai, organizations can reduce the financial and resource drains that accompany all the tasks involved in remediation of a credential stuffing attack. These include replacing stolen assets, investigating compromised accounts, reporting to regulatory authorities, and handling user complaints.
Additional Akamai defenses against botnets
Akamai offers several additional cybersecurity solutions that can help to defend against botnet attacks.
- Akamai Bot Manager offers unmatched detections and mitigation capabilities that permit traffic from good bots while stopping malicious bots where they make initial contact, rather than allowing them to reach websites first. Bot Manager’s detections and analytics are constantly updated with insights from Akamai’s threat intelligence researchers. And Bot Manager delivers comprehensive protection — on endpoints via web browser, native mobile apps, and APIs, and even when requests cross from one domain to another.
Akamai Prolexic stops DDoS attacks from botnets in the cloud, before they reach applications, data centers, operating systems and internet-facing infrastructure. With 20+ global high-capacity scrubbing centers, Prolexic stops attacks closer to the source to maximize performance for users and maintain network resiliency through cloud distribution.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A bot is a piece of software programmed to automatically perform specific tasks, often highly repetitive activities that can be performed with greater speed and precision than human users can offer. Bots are used for both productive and malicious purposes. Good bots include spiders or web crawlers that index content on websites for search engines, while chatbots help customers access the information they need on websites. Bad bots may scrape content from websites, hoard inventory, or artificially drive up traffic on websites and social media accounts.
A botnet is a group of computers, machines, or Internet of Things (IoT) devices that have been infected with malware that places them under the control of a cybercriminal or “bot herder.” A botnet may comprise thousands or even millions of infected machines, which can be used to target vulnerabilities in software or send phishing emails. Different types of botnets are often used in cybercrime like distributed denial-of-service (DDoS), credential stuffing, and brute-force attacks that help attackers gain unauthorized access to IT environments.
A bot coordinator is an individual or group who is responsible for controlling a botnet, a network of computers infected with malicious software and controlled as a group without the owners’ knowledge or permission. The botnet coordinator can use the botnet to launch DDoS attacks, steal data, and spread malware.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.