Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.
A content delivery network (CDN) is a group of interconnected servers distributed around the world that accelerate the delivery of web content by serving it from locations closer to users. By storing copies of files — a process called caching — CDNs minimize the time it takes for content like web pages, images, and video to reach a user’s device. This prevents users from having to wait for content to load as they watch movies, download software, make purchases, or perform other tasks online. A cloud CDN is a CDN that uses distributed cloud-based compute, storage, and networking resources. Many cloud services providers offer CDNs as part of their platforms.
How did CDNs originate?
In 1988, Akamai launched the first generation of CDNs to solve the problem of network congestion caused by increasingly rich web content such as graphics and video. Accessing this bandwidth-intensive content from centrally located servers was causing online traffic jams and degrading the user experience. Subsequent generations of CDN services focus on more complex web and multimedia content at increasingly affordable rates.
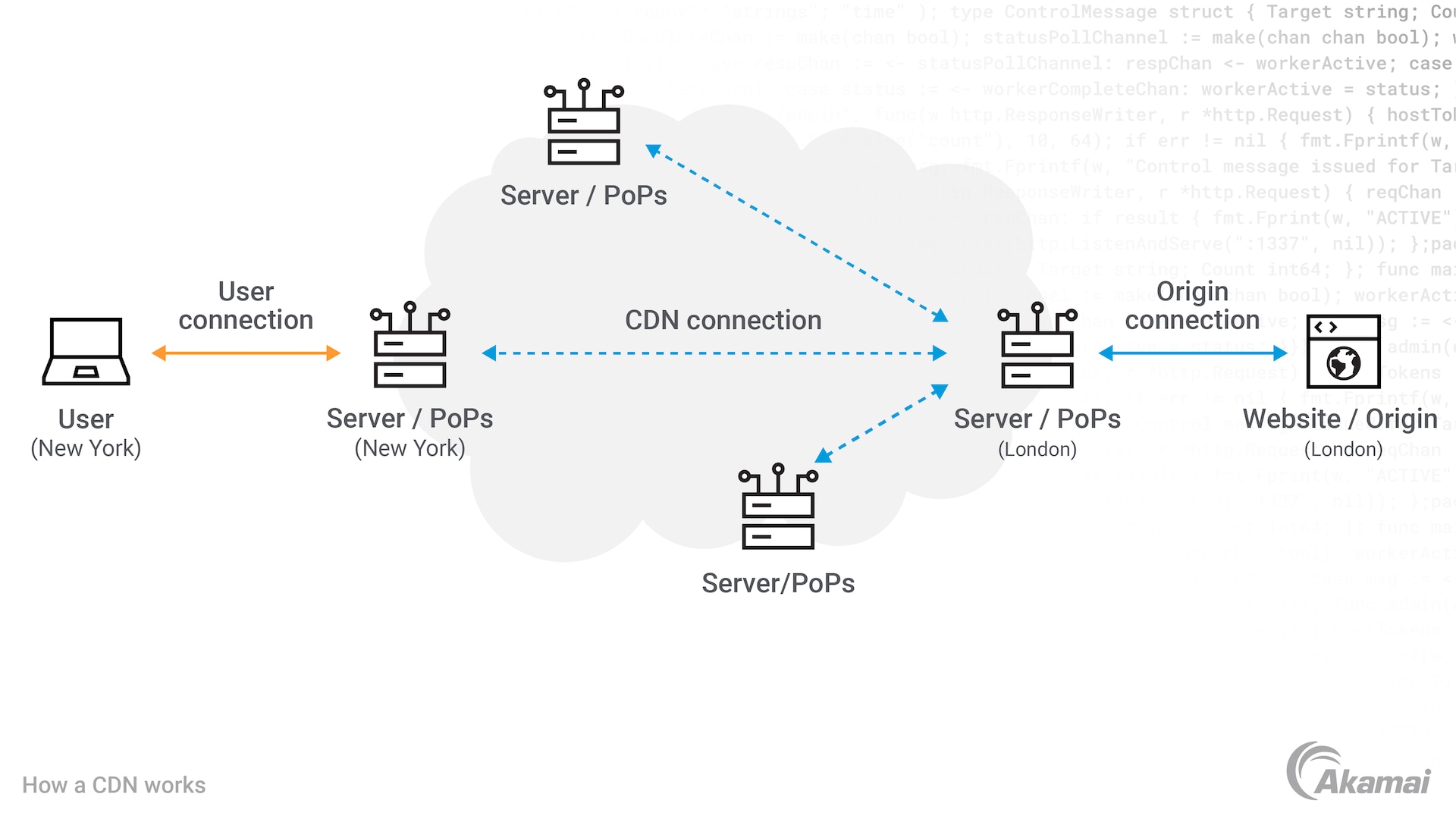
How does a CDN work?
The purpose of a cloud CDN is to minimize latency, which prevents the delay that users experience when they try to access a web page or streaming video. Even small delays can cause enormous frustration for users who have ever higher expectations about how quickly content should be loaded. To avoid this, CDNs cache content in servers located around the world, and route content requests from users to the server that can deliver it most quickly. When one server becomes congested, a CDN will route content around it to another server that can deliver it faster.
What are the components of a cloud CDN?
- Points of presence (PoPs) are data centers distributed around the world that serve content to nearby users. PoPs reduce the time required to serve content to a user’s device.
- Servers with large amounts of storage and RAM store and deliver cached files to users, accelerating the load times of websites and reducing bandwidth consumption.
- Cloud load balancing technology seamlessly directs traffic to the PoPs that can serve content to a user fastest, evenly distributing the load across cloud resources and achieving greater cloud optimization.
- Solid-state drives (SSD), hard disk drives (HDD), and random-access memory (RAM) within cloud CDN servers store files to be served, with the most requested files being stored on the fastest media.
How does a CDN improve online experiences?
Many online experiences rely on dynamic web content that can change with every user request. Caching static copies of this content is impossible. To accelerate response times, CDNs can forward the request to the original server through a trusted, established connection that elicits a faster response.
What are the benefits of a CDN?
- High performance. CDNs improve the performance of web content, high-quality video, audio streams, software downloads, and other online experiences.
- Greater availability. Superior cloud CDNs can absorb massive amounts of traffic from users while still serving content at an optimal rate.
- Better security. Distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks and web-based exploits not only threaten organizations but the online experience for users as well. CDN systems have made DDoS protection and cloud-based security a core competency, providing cloud-based security solutions to protect content providers and users by mitigating a wide array of attacks that could compromise delivery and availability.
- Lower cost. Serving content from traditional clouds can incur significant data egress charges. CDNs reduce cost by reducing bandwidth consumption and the significant expense associated with purchasing bandwidth.
What are the use cases of the cloud CDN?
- Delivering content at high speeds. Using a cloud CDN, content providers and media companies can deliver content to users much more quickly, providing high-quality, low-latency online experiences.
- Improving the quality of streaming media. Companies that deliver audio and video streaming rely on CDNs to reduce delivery time, minimize bandwidth costs, and scale up to meet user demand as needed. Streaming video services especially benefit from cloud CDN technology that enables them to meet spikes in demand when certain video content becomes quite popular.
- Scaling up for multiple users. From gaming companies to SaaS and business productivity platforms, the scalability of CDNs enable millions of users to access a website or platform simultaneously without experiencing degraded performance.
Who uses a CDN?
CDNs are increasingly the backbone of the internet’s best applications. Websites and web applications delivered through cloud CDNs enable faster page loads and improve online experiences. Content owners such as ecommerce sites, media properties, and cloud computing companies rely on CDNs to improve customer experiences, reduce abandonment rates, enhance conversion rates, and build greater customer loyalty. For network service providers that offer video streaming and rich media services, CDNs help reduce subscriber churn, minimize traffic on the core network, and enable operators to sell services to enterprises and third-party content owners.
What is cloud computing vs. cloud CDN?
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to computing, storage, and networking resources with a pay-as-you-go pricing model. Clouds rely on hundreds of data centers around the world with virtualized machines running on servers that allow multiple users to access computer resources as needed. A cloud CDN is a collection of servers that distribute content from an origin server throughout the world, caching content close to where each end user will access it. By caching content physically close to the users that request it, CDNs help to significantly reduce latency.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A cloud CDN is a network of servers that distributes content from an origin server throughout the world, storing or caching content close to where each user will access it. Cloud storage is a cloud computing service model where organizations can store content in remote cloud servers managed by cloud providers to reduce costs, minimize IT burden, enhance backup and disaster recovery efforts, simplify compliance, and streamline archiving and record retention.
A cloud CDN uses cloud computing resources to connect users with content cached close to their location. A telco CDN uses telecommunications infrastructure to connect users throughout a content delivery network.