Like PaaS solutions, serverless computing lets developers create applications without needing to manage servers or back-end infrastructure. Serverless solutions scale more easily than PaaS offerings, but developers have less control over a serverless environment than a PaaS solution.
An introduction to cloud platforms
A cloud platform is the operating system and hardware of servers in a data center that are configured to provide cloud computing services to customers. A cloud platform enables businesses to rent access to computing resources on demand over the internet with pay-as-you-go pricing, rather than buying, installing, and managing their own data centers, servers, and software required to have these resources available on premises.
How does a cloud platform work?
Cloud platforms create a virtual pool of shared resources to provide compute, data storage, and network services over the internet. Customers can access resources on the cloud platform as needed, paying only for the resources they need. Cloud platforms use virtualization technologies that create multiple virtual machines, or VMs, on a single server, making it possible to run separate operating systems and applications for various customers on one physical server. Customers may access compute services from both public and private cloud platforms. Cloud platforms allow organizations to store, back up, and recover data; test and build apps; access cloud databases; analyze big data sets; deliver software on demand on a global scale; access business intelligence; and create cloud-native applications.
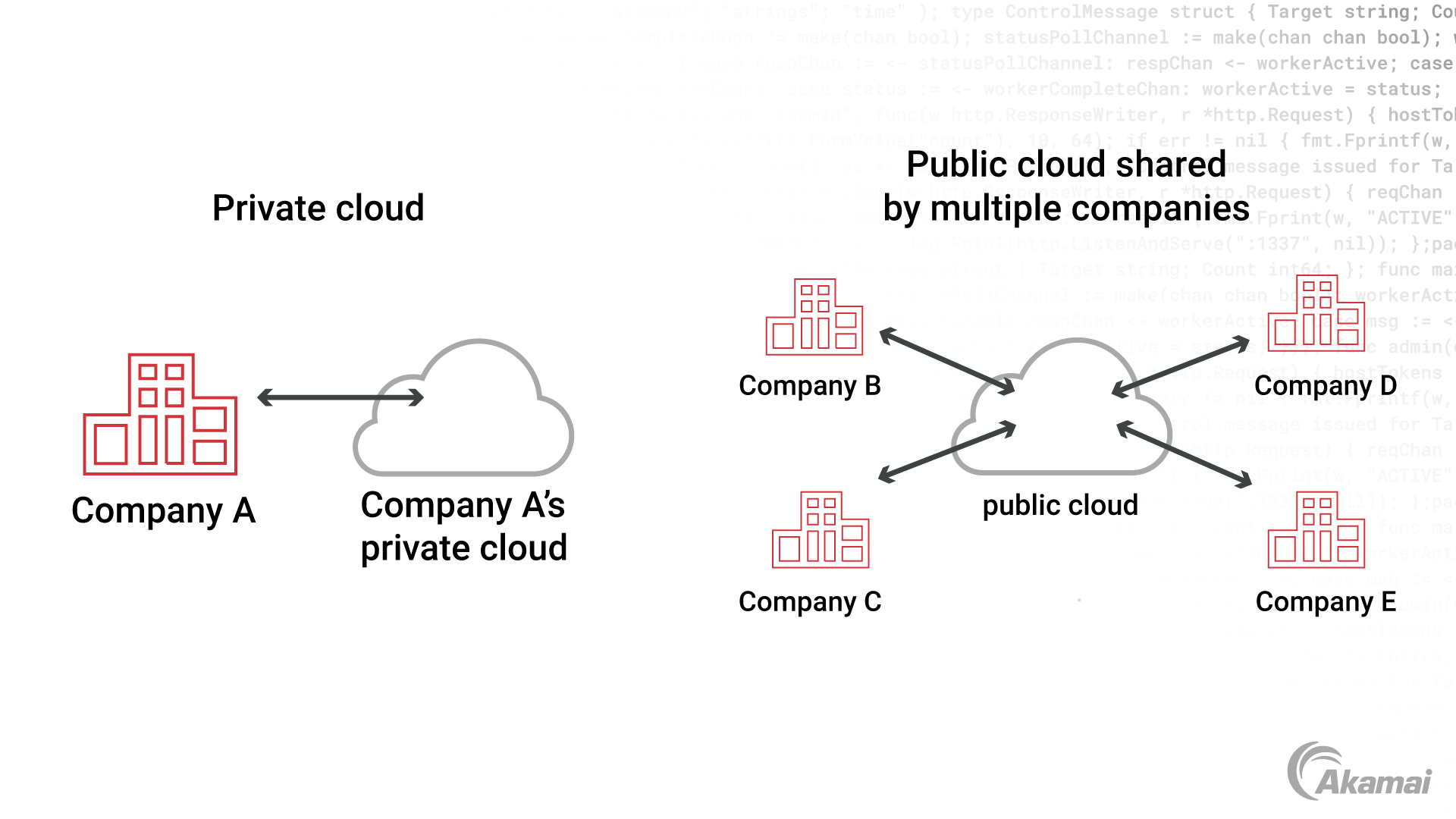
What is a private cloud platform?
A private cloud platform is a cloud computing environment dedicated to a single organization. A private cloud may be owned and managed by the organization or leased from a private cloud provider. In contrast to the multitenant environment of a public cloud — where multiple organizations may be renting and competing for computing resources on one physical server — a private cloud is a single-tenant or “bare metal” environment, where the organization using a private cloud will never have to compete for resources with other customers.
What is a public cloud platform?
A public cloud platform is operated by a cloud services vendor, a third-party provider who owns, manages, and upgrades the hardware and software for the cloud platform. The resources on a public cloud platform are available to anyone. Public cloud providers typically service multiple customers through virtual machines that are isolated from one another on the same physical server.
What are the benefits of a cloud platform?
Cloud platforms and cloud computing solutions offer businesses a variety of advantages.
- Greater elasticity. By accessing computing services from a cloud platform rather than on-premises technology, organizations can scale up and down incredibly quickly to meet business requirements, avoiding the risk of over- or under-provisioning.
- Reduced costs. Cloud platforms enable businesses to eliminate the capital expense of establishing an on-premises data center as well as the cost of IT staff to manage it. Cloud platforms also allow organizations to pay only for the cloud resources they consume, contributing to significant cost savings.
- Stronger performance. Cloud platforms can deliver superior performance by allowing businesses to access all the compute power and cloud storage they need on demand. Virtualized pools of cloud-based resources and solutions for cloud load balancing help to avoid bottlenecks.
- Increased agility. The on-demand resources available from cloud platforms enable businesses to deploy the exact cloud infrastructure they need at any given moment to speed innovation and time-to-market.
- Faster deployment. Cloud computing resources allow businesses to deploy the technologies they need anywhere in the world in a matter of minutes, rather than days, weeks, or months.
- Enhanced productivity. Because cloud platforms are managed by third-party providers, IT teams are freed from the responsibility of managing, maintaining, and upgrading hardware and software on site.
- Tighter security. Cloud service providers invest heavily in cloud security technologies to defend their platforms from threats and outages, providing stronger security than most organizations can implement for their own data centers.
- Superior reliability. Because they are built with a vast and virtualized pool of resources, cloud platforms are more resilient than on-site data centers. Distributed cloud platforms involve multiple servers and multiple sites around the world to ensure even greater reliability and enable faster disaster recovery.
- Advanced mobility. Cloud platforms support the trend to remote and hybrid workforces by making compute resources available to employees anywhere, any time via the internet.
What are the advantages of public cloud vs. private cloud platforms?
Both public cloud and private cloud platforms deliver all the benefits of cloud computing, including on-demand, self-service provisioning of highly scalable compute resources.
Public clouds offer near-infinite scalability and superior cost-effectiveness, as organizations pay only for the resources they consume and are not responsible for purchasing, installing, or maintaining any equipment. On the other hand, organizations utilizing public clouds may compete for resources with other customers who are using resources on the same physical server.
Private clouds offer more control and customization over dedicated resources while providing a higher level of security and privacy. One drawback of private clouds is that they require a greater investment in hardware and software (when the cloud platform is owned by the organization), and they require more management and supervision from an internal IT team. Private clouds do not offer the same level of scalability as public clouds.
Many organizations opt for a hybrid cloud approach, deploying workloads on a mix of public and private cloud platforms to take advantage of the benefits of both types of environments. Many businesses also opt for a multicloud environment, using two or more public or private cloud platforms from two or more cloud service providers to increase resiliency and to access the exact services they need.
What is a cloud platform as a service?
Platform as a service (PaaS) offerings provide on-demand access to a cloud platform for software development teams. Developers use PaaS solutions to build, test, and run software applications without needing to build or maintain the infrastructure to support these activities. PaaS offerings include computing infrastructure — servers, virtual machines, storage, and networking services — as well as the runtime, middleware, and operating systems that are part of an application development environment.
What is serverless computing?
Like PaaS solutions, serverless computing lets developers create applications without needing to manage servers or back-end infrastructure. Serverless solutions scale more easily than PaaS offerings, but developers have less control over a serverless environment than a PaaS solution.
What are the limitations of cloud platforms?
Because cloud platforms are accessed over the internet, there is always a risk of downtime from outages or poor performance from sluggish connections. Businesses using public cloud platforms have less control over their data and computing resources than with an on-site data center. Security can also be an issue. Cloud platform providers offer best-of-breed security solutions, but they operate with a shared responsibility security model that is often misunderstood by customers, leading to security gaps when IT teams don’t understand their own role and responsibility for securing the data and assets within their controls.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cloud computing refers to computing resources like processing, storage, and networking made available on demand to customers over the internet. A cloud platform is the hardware, software, and operating system within one or more data centers that makes cloud computing possible.
A content delivery network, or CDN, is a geographically distributed network of points of presence (PoPs) that can serve content from locations close to users. By caching content like web pages, images, and video in a variety of proxy servers in different locations, CDNs can serve content to users faster, reducing latency and enabling better online experiences. A cloud CDN relies on cloud computing resources to manage and operate a CDN, rather than on telecommunications services.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.