In addition to securing your Memcached server, you can also use a DDoS mitigation service like Akamai Prolexic to protect your website from DDoS attacks.
Memcached DDoS Explained
In recent years, we’ve seen a trending rise in the number and sophistication of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attacks. One tactic that attackers use to amplify their attacks is to exploit vulnerabilities in Memcached servers. In this article, we’ll explain how the Memcached DDoS works, why it’s so effective, and what you can do to defend against it.
What is Memcached?
Memcached is a high-performance, open-source, distributed memory and database caching system. The key-value is often used to speed up dynamic websites and web applications by caching frequently accessed data in memory. Memcached is widely used by companies like Facebook, Twitter, and YouTube. Memcached also has UDP support and is a main contributor to the attack vector.
What is a DDoS attack?
A distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack is a type of cyberattack where a large number of compromised devices (called a botnet) flood a target website or server with traffic. Hackers use the sheer volume of traffic that overwhelms the target, making it inaccessible to legitimate users or functions like authentication.
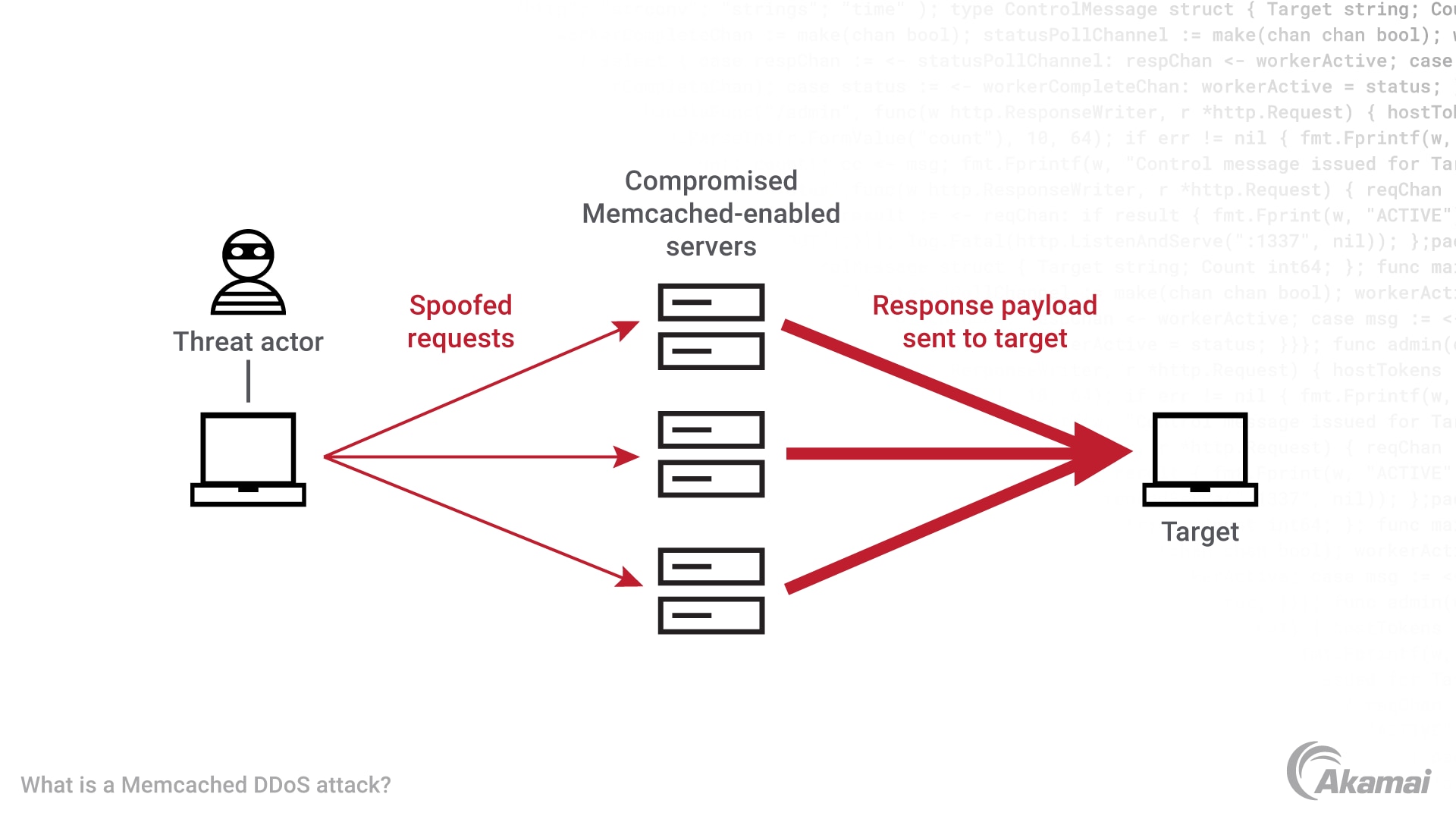
What is a Memcached DDoS attack?
Memcached attacks are a type of amplification attack where an attacker sends an HTTP GET request to a vulnerable Memcached server. In return, the vulnerable server sends UDP packets towards the intended target with large amplification factors. Cybersecurity experts estimate that some Memcached amplification can reach 51,000x the initial “GET” request asking it to return a large amount of UDP data. The request is designed to spoof the source IP address, making it appear to come from the victim’s IP address. When the Memcached server responds, it sends the data to the victim’s IP address, amplifying the traffic and overwhelming the victim’s server.
How does a Memcached DDoS attack work?
Here are the steps involved in a Memcached DDoS attack:
- The attacker scans the internet for vulnerable Memcached servers.
- The attacker sends a small HTTP GET request to the exposed Memcached server, asking it to return a large amount of data UDP Memcached payloads. The request is designed to spoof the source IP address, making it appear to come from the victim’s IP address.
- The Memcached server responds to the request by sending the large amount of data to the victim’s IP address.
- The victim’s server at the data centers is overwhelmed by the malicious reflection attack traffic, making it inaccessible to legitimate users.
Why is a Memcached DDoS attack so effective?
A Memcached DDoS attack is effective because it can amplify the payload of attack traffic by a factor of up to 50,000 times. This means that a small request can result in a huge amount of traffic being sent to the victim’s server or data center. In addition, Memcached servers are often connected to high-speed networks, which means that the traffic can be sent very quickly, making it harder to defend against. Another common reason is that the attacker does not have to maintain their own infrastructure to generate DDoS attacks. Attackers can leverage open internet resources for IP spoofing, UDP port attacks, and other targeted endpoints. Akamai’s recorded largest DDoS attack included over 1 Tbps worth of attack traffic from the memcached protocol.
How to defend against a Memcached DDoS attack?
Here are some options you can use to protect yourself from a Memcached DDoS attack:
- Disable UDP: Memcached servers use the UDP protocol by default, which can be easily spoofed. By disabling UDP and only allowing TCP, you can prevent spoofed requests from reaching your Memcached server.
- Firewall: You can also use a firewall to block incoming traffic from known malicious IP addresses to your Memcached server.
- Rate limiting: Another option is to implement rate limiting on incoming traffic to prevent spikes in traffic to your Memcached server.
- Update Memcached: Make sure you are running the latest version of Memcached, which includes security patches.
- Targeted directly with Memcached DDoS: Leverage cloud DDoS protections for this type of attack. Given the high amplification factor and number of open Memcached servers, implementing local mitigations at the data center can lead to capacity issues.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
No, Memcached is not the only service that can be used in amplification attacks. Other services like DNS, NTP, and CLDAP have also been used in similar attacks.
You can use a vulnerability scanner to test your Memcached server for vulnerabilities. If it is found to be vulnerable, you should take steps to secure it as soon as possible.
Prevent Memcached and other DDoS attacks
Memcached DDoS attacks are a serious threat that can be used to bring down websites and servers. Attackers can exploit vulnerabilities in Memcached servers to amplify their attacks and overwhelm their targets. However, by taking steps like disabling UDP, implementing rate limiting, and keeping your Memcached server updated, you can protect yourself from these attacks. It’s important to stay vigilant and keep your defenses up to date to stay protected in the ever-changing landscape of cyberattacks.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.

