A cloud platform is made up of the hardware and software in a data center that provides on-demand access to computing resources like servers, databases, storage, analytics, networking, and applications via the internet.
An introduction to hybrid cloud
Hybrid cloud has become a dominant technology in enterprise cloud computing. More than 80% of IT leaders report that their companies have adopted a hybrid cloud approach, while only 8% of organizations continue to use a single public IaaS provider. This brief introduction to hybrid cloud services offers an overview of the technology and its benefits for businesses.
What exactly is hybrid cloud?
Hybrid cloud is a computing model that uses a mix of public cloud, private cloud, and on-premises infrastructure to provide a broad range of cloud computing services. In a hybrid cloud, workloads can migrate seamlessly between public cloud services, private cloud technology, and on-premises infrastructure to improve performance, reduce risk, and minimize costs. To understand how a hybrid cloud works, it’s helpful to first understand cloud computing, public clouds, and private clouds.
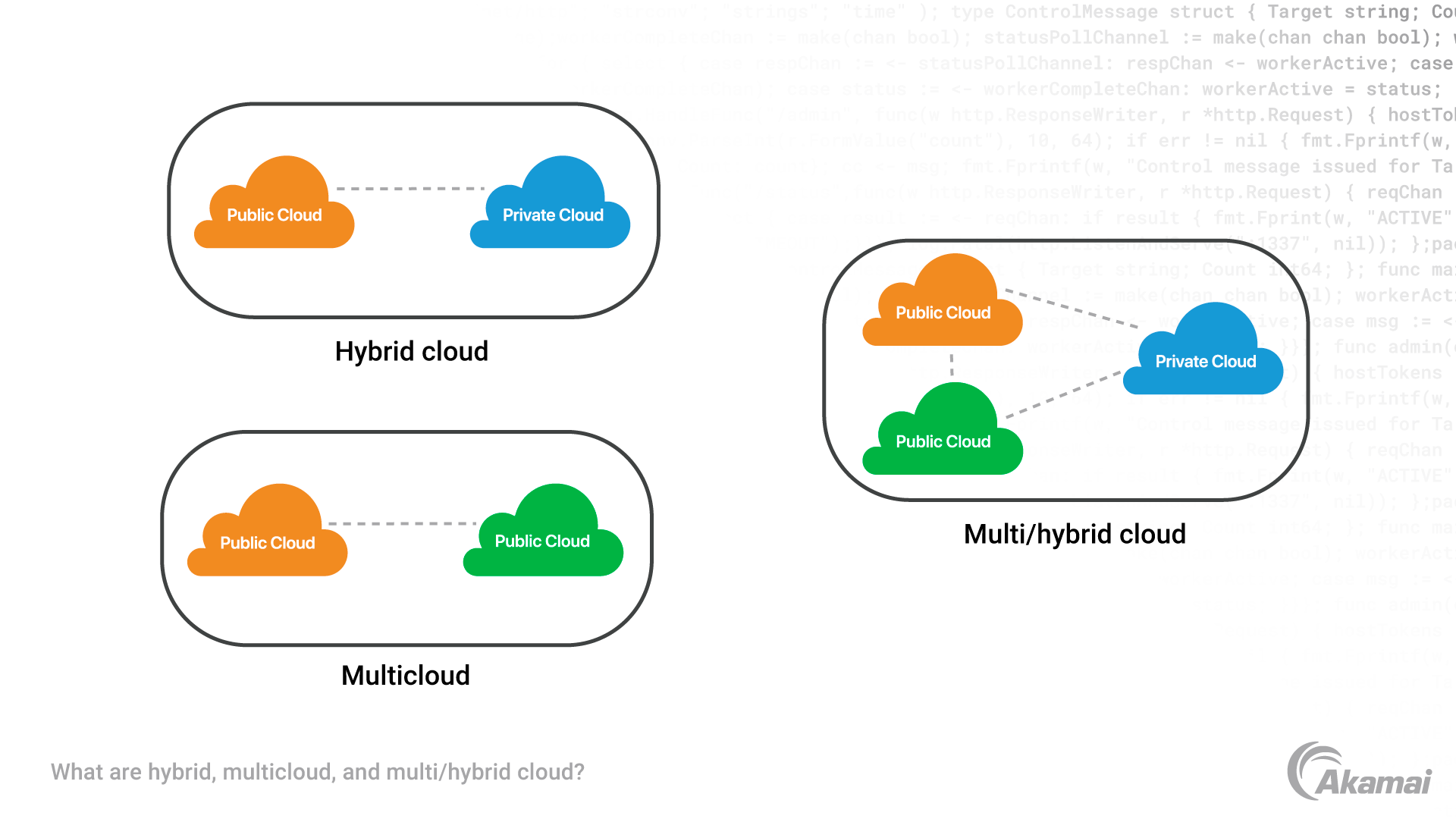
What is the cloud?
In cloud computing, third-party providers offer access to IT infrastructure like computer processing, data storage, networking, applications, and databases via the internet, allowing businesses to avoid purchasing, installing, and managing their own hardware and software. Cloud services offer pay-as-you-go pricing, on-demand self-service, and rapid elasticity that enable businesses to quickly provision IT infrastructure in the cloud and scale up at a rate that is not possible with on-premises infrastructure.
What is public cloud?
Public cloud services are offered by third-party providers from data centers anywhere in the world. In a public cloud environment, many organizations/customers share the same infrastructure, enabling providers to offer services at highly cost-effective rates. This is made possible by virtualization technologies that allow multiple virtual machines (VMs) to operate on a single server, making it easy to aggregate IT technologies into shared pools of resources. Public cloud providers and hyperscalers like Google Cloud, Microsoft Azure, and AWS offer massive economies of scale, providing cost-efficiencies that on-premises data centers simply can’t achieve.
What is private cloud?
Private clouds use the same virtualization technology to provide scalable, on-demand IT resources that can be quickly provisioned by users. But private cloud environments are dedicated to serving the needs of one organization, rather than sharing resources among multiple customers or “tenants.” As a result, private clouds provide more control over data and security, helping organizations to meet specific regulatory and compliance requirements. Because IT teams retain control over private clouds, they can more easily customize the infrastructure to meet the specific needs of the business.
How does hybrid cloud work?
Hybrid cloud architecture is designed to provide greater flexibility for companies using cloud services. A hybrid cloud combines public cloud and private cloud environments, frequently in combination with on-premises infrastructure. In contrast to a multicloud environment where cloud services are managed separately, a hybrid cloud strategy focuses on integrating cloud environments to promote workload portability. Hybrid cloud eliminates reliance on any single cloud provider and allows businesses to match each workload or application to the cloud resources that can best achieve objectives for performance, regulatory requirements, and cost.
For example, businesses may choose to run highly sensitive or business-critical workloads on private clouds where they have more control over the infrastructure and regulatory compliance. Public clouds may be used for inexpensive cloud storage as well as dynamic workloads that require greater flexibility, on-demand scalability, and massive data processing power.
What are the characteristics of hybrid cloud?
Hybrid cloud solutions are distinguished by several characteristics:
- They connect multiple computers and computing resources on a single network.
- They consolidate IT resources into shared pools.
- They allow workloads to move seamlessly between environments as business needs dictate.
- They can be managed with a single, unified solution.
- They retain the capability of cloud computing to provide on-demand access to highly scalable computing resources.
What are the benefits of hybrid cloud?
A hybrid cloud strategy offers many advantages over public or private cloud deployments.
- Cost savings. The ability to run certain workloads on public clouds can help to significantly reduce expenses, increase efficiency, and eliminate waste.
- Optimal security. Hybrid clouds allow businesses to keep their most sensitive data within the confines of a private cloud while taking advantage of the advanced security measures offered by public cloud providers to protect less business-critical assets.
- Massive scalability. Businesses can rely on the public cloud component of a hybrid environment to handle workload bursts and spikes in demand.
- Greater control. Orchestration and automation technologies help IT teams to manage and optimize workloads more efficiently to achieve superior performance at a lower cost.
- IIncreased agility. With technology that can meet changing business demands more easily, businesses can innovate more easily and compete more effectively.
- Business continuity. Hybrid clouds promote business continuity by automating backups, absorbing spikes in traffic, and accelerating disaster recovery.
- Incremental cloud migration. A hybrid approach allows organizations to move to the cloud at an ideal pace, running workloads on the preferred cloud or on-premises infrastructure, rather than being forced to move everything to a single public or private cloud environment.
- Future-proof flexibility. When business needs or market opportunities arise, a hybrid cloud provides flexibility that allows businesses to respond faster and more easily.
What are the challenges of hybrid cloud?
For all their benefits, hybrid clouds offer several challenges as well.
- Capital expense. The private cloud component of a hybrid strategy requires businesses to invest in the hardware and software components that comprise a private cloud, along with the IT expertise to manage it.
- Management complexity. Managing hybrid cloud infrastructure typically means working with multiple vendors and platforms and managing the movement of workloads between different environments — a highly complex task. Multiple cloud environments also limit visibility, and can make it more difficult to monitor and manage the systems, processes, platforms, applications, compliance, and other requirements within a hybrid cloud.
- Security concerns. Because hybrid clouds are more complex to manage, there’s a risk that IT teams may not adequately stay on top of security controls, policies, and hygiene.
What are hybrid cloud use cases?
Hybrid clouds can serve a wide range of use cases.
- Development and testing. The public cloud component of a hybrid strategy allows development teams to build and test applications much faster and more efficiently.
- Strict regulatory environments. Sensitive data and highly regulated workloads can be run on private cloud resources to ensure compliance while moving less-sensitive workloads and data to economical public cloud environments.
- Rapid adoption. Hybrid clouds make it possible to onboard new SaaS solutions, giving users access to the latest technologies while still running legacy applications from on-premises or private cloud environments.
- Disaster recovery. Hybrid solutions can fine-tune disaster recovery by optimizing backup processes and bandwidth requirements while reducing local storage space and minimizing costs.
- Digital transformation. Hybrid cloud computing allows companies to modernize certain aspects of their IT infrastructure while continuing to use legacy applications that won’t migrate easily to the cloud.
- Dynamic workloads. Hybrid cloud environments allow businesses to easily move between public and private clouds as the computational power for various workload changes.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cloud computing provides on-demand access to highly scalable computing resources such as servers, storage, and networking. Accessed via the internet or a network connection, cloud resources enable organizations to avoid purchasing, installing, managing, and upgrading their own computer hardware and software in on-premises data centers.
Cloud infrastructure refers to the technologies that enable cloud computing, including server hardware, data storage devices, network resources, and interfaces that allow users to access virtualized resources.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.

