Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.
An introduction to multicloud computing
A multicloud approach has become the dominant strategy for organizations embracing cloud computing. Multicloud environments combine two or more public or private cloud services, enabling organizations to optimize performance, minimize costs, and leverage superior technology.
This brief introduction offers an overview of the multicloud strategy and its benefits for businesses large and small.
What is multicloud computing?
Multicloud deployment is often preferred by businesses, sometimes without the business recognizing it is adopting the technology, but doing so because it addresses the business requirements. It’s association by need, not design.
The defining aspect of the multicloud setup is that it makes use of multiple public cloud services. These services often come from different providers, all of which make their offerings publicly available. So your company might use any combination of AWS, Google Cloud, Azure, Linode, DigitalOcean, or Rackspace. For example, your groupware might be hosted on Google Cloud (such as Google Workspaces), your mobile applications on AWS, your containerized applications on Linode, your website on Azure, and your storage on DigitalOcean. That’s a widespread multicloud deployment, but it illustrates how multicloud can work.
One reason to spread your technology net so wide is because one cloud provider doesn’t support all of the technologies your business requires to function. Another reason could be that it’s more cost-effective to run a particular type of workload on one platform than the others.
IT decision-makers align company business technology adoption with a need and solve that need with a solution. In the modern IT landscape, that solution is often handled via the cloud. Given how many pre-built services exist within the cloud, the decision is not difficult. Problem X + Cloud Solution Y = Reliable Workflow.
What is public cloud?
In a public cloud, computing resources are hosted by a third-party provider, or cloud service provider (CSP), from data centers that may reside anywhere in the world. Public cloud infrastructure can run many virtual machines (VMs) on a single physical server to provide computing resources to multiple customers or “tenants” at the same time. This “multi-tenant” approach allows public cloud providers to cost-effectively offer nearly unlimited resources that can be provisioned within minutes by users, without intervention from IT teams. Public cloud services are usually offered on a pay-per-usage model.
What is private cloud?
A private cloud is a cloud environment that is dedicated to serving one organization. Private clouds offer the benefits of cloud computing, including self-service provisioning, easy scalability, and resources on demand. But because services are provided from hardware that is managed by the organization, private clouds offer greater control and security, especially for organizations that must comply with strict regulatory compliance requirements. Unlike multi-tenant public clouds, private clouds are a “single tenant” solution, meaning that organizations will never have to compete for resources with other customers renting space on the same servers.
How does multicloud work?
A multicloud environment typically uses two or more public cloud services or two or more private clouds. Multicloud deployments are established by contracting with separate cloud providers. To deliver maximum value, multicloud infrastructure should be managed centrally, as if the separate environments were part of a single cloud.
What is multicloud architecture?
A multicloud environment is usually built on one of three models.
- Distributed multicloud architecture allows businesses to choose vendors based on their offerings and to distribute workloads across vendors based on their suitability.
- Redundant multicloud architecture ensures business continuity by automatically routing traffic to a secondary cloud service when a primary cloud vendor experiences a failure or outage.
- Intercloud architecture enables workflows and data to move from one public cloud to another, as long as the cloud services are integrated.
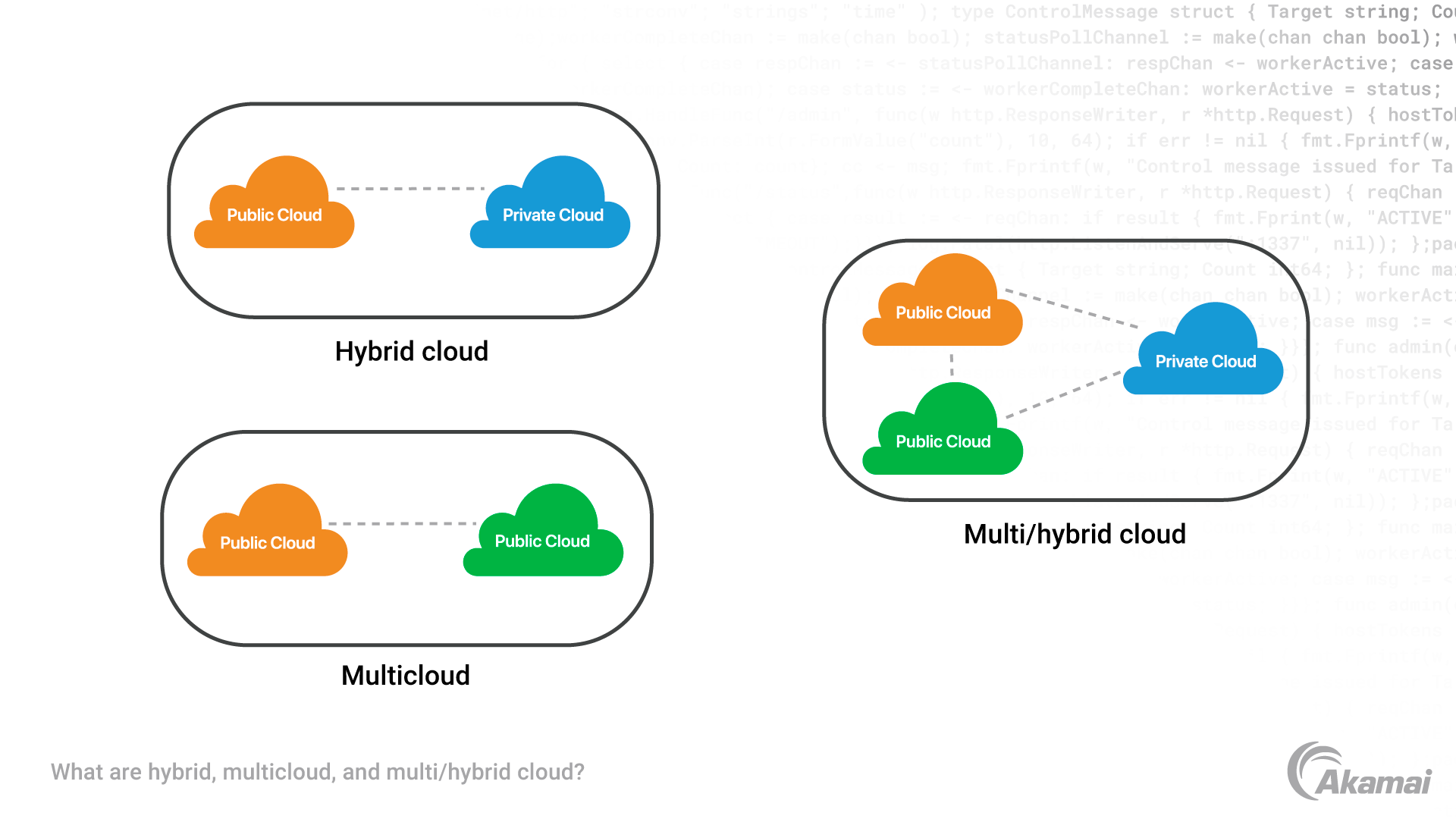
What is multicloud vs. hybrid cloud?
While a multicloud environment comprises two or more distinct cloud services, a hybrid cloud combines public cloud and private cloud services in an integrated environment that allows workloads to move seamlessly between cloud platforms as well as on-premises infrastructure.
What are the benefits of multicloud environments?
Multicloud solutions can help organizations achieve several key objectives.
- Accessing the best solutions. Because no single cloud provider offers solutions for every aspect of the business, many companies prefer to use multiple providers to access best-of-breed solutions for various areas of the business.
- Avoiding vendor lock-in. When using a single cloud vendor, there is always a risk of becoming overly reliant on one solution, leading to increased costs and lack of flexibility.
- Supporting edge computing. Companies may choose multiple providers in an effort to distribute applications at the edge, closer to physical devices and users.
- Minimizing the impact of outages. Since an outage on one cloud won’t necessarily impact other clouds, a multicloud approach reduces the risk of unplanned downtime.
- Competitive pricing. Multicloud environments allow organizations to secure the best rates from different vendors based on specific IT needs.
- Long-term savings. By running each workload in the cloud environment that is most cost-effective, organizations can significantly reduce the cost of consuming IT resources over time.
What are the challenges of a multicloud strategy?
- Management complexity. Multicloud deployments inevitably require IT teams to interface with different vendors, adding a layer of complexity to cloud management. Various cloud platforms may require different workflows and management tools, creating headaches for IT teams. Visibility may be more difficult in a multicloud environment, complicating efforts to optimize workloads and troubleshoot issues.
- Increased latency. Latency can result when services must communicate with each other across multiple clouds that are not tightly integrated.
- Larger attack surface. If security controls are not properly deployed, multiple cloud solutions may result in an IT environment with more points of vulnerability.
- Skill shortages. Managing multicloud infrastructure requires expertise and specific skills that existing IT teams may not possess — and that may be hard to source without having access to strong customer support teams.
- Compatibility. Since various cloud platforms often rely on different APIs and architectures, managing workloads and synchronizing and sharing data across multiple environments can be difficult.
How are multicloud environments managed?
Organizations can use multicloud management tools to simplify monitoring, management, and orchestration of multicloud environments. Ideally, multicloud management solutions should deliver visibility into and control over any cloud resource, including SaaS, IaaS, and PaaS solutions as well as data storage and networking resources. Analytics can help to streamline operations, prevent performance issues, predict availability, and automate many management tasks across a multicloud infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
“Multicloud” simply means the use of cloud services from two or more vendors. Multicloud deployments can be as simple as subscribing to several software as a service (SaaS) solutions from different cloud providers, or they may involve running a variety of complex enterprise applications by using separate cloud providers for various components.
Hybrid cloud computing is a type of cloud computing that combines public cloud services with private cloud, or on-premises, resources. It allows organizations to use a mix of cloud services, applications, and resources that are managed both internally and externally. Hybrid cloud computing provides businesses with the flexibility to scale and manage their workloads across multiple platforms while still keeping data and applications secure.