In computing, the cloud is a vast network of computer servers in data centers around the world. Accessible via the internet, servers in the cloud provide organizations and users with on-demand computing resources like processing, data storage, networking, databases, applications, and analytics. Cloud computing uses virtualization technology that makes it possible to create a shared pool of resources that can scale easily to accommodate the needs of businesses and end users anywhere in the world. Cloud computing services offer a cost-effective way for businesses to access as much computing power as they need without purchasing, installing, and managing their own hardware and software.
An introduction to private cloud
As organizations seek to take advantage of enterprise cloud computing, their primary options are between public and private cloud offerings. While the many advantages of the public cloud are constantly promoted by public cloud providers, the benefits of private cloud technology are less well-known. This brief introduction to the private cloud offers an overview of the technology and its benefits for organizations and IT teams.
What is private cloud?
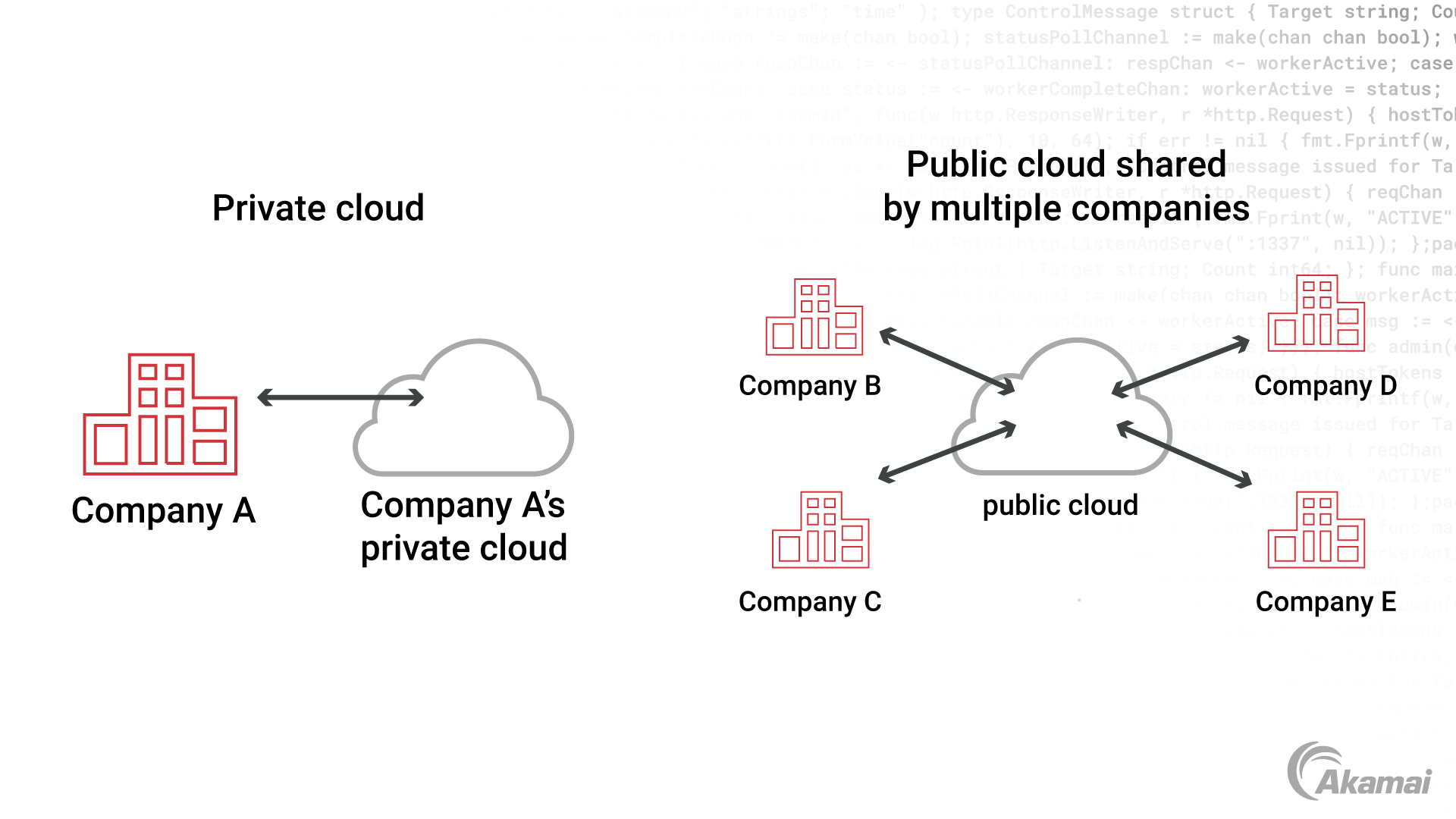
Private cloud is a cloud computing environment that serves a single customer. Where the services of public clouds are available via an internet connection to any organization, a private cloud can be accessed only by users within the organization that owns it. Combining the benefits of the public cloud with the security and control of on-premises infrastructure, a private cloud can be hosted within an organization’s own data center, at a third-party facility, or through a private cloud provider.
How do private clouds work?
Private cloud is based on the same technologies as public cloud. Virtualization technology makes it possible to combine computing resources from a broad array of physical hardware, creating a shared pool of resources that can be easily accessed by users. Management and orchestration technologies provide centralized control over hardware and software, and automation enables cloud resources to be delivered through self-service. However, in contrast to a multi-tenant public cloud — where multiple customers use virtualized resources that exist on the same server — a private cloud is a single-tenant environment. Consequently, an organization utilizing a private cloud will never have to compete for resources with other customers.
What are the benefits of private cloud?
In addition to the general advantages of cloud computing, a private cloud environment offers additional benefits.
Tighter security. While public clouds offer advanced security measures to protect data from theft and loss, private clouds provide full control over data and computing infrastructure. Additionally, the data within a private cloud is not accessible by third-party providers, as it may be within a public cloud.
Improved performance. With a private cloud, the organization’s workloads are not competing for resources with the workloads of other customers.
Predictable costs. The costs of a private cloud tend to be more transparent and predictable than public cloud pricing.
Long-term value. Though the cost of building private cloud infrastructure may require substantial upfront costs, this investment can yield significant dividends over time through improved performance.
Easier customization. Because private clouds offer complete control over the architecture and operations of cloud resources, organizations can more easily customize private cloud deployments for their needs.
Regulatory governance. For businesses in heavily regulated industries, private cloud infrastructure may make it easier to comply with strict regulations regarding the storage and use of sensitive data.
Improve utilization. Virtualization in a private cloud improves resource utilization by allowing underused servers to be made available for any workload in any part of the organization.
Support for legacy technology. Private clouds may be a better option for legacy applications that can’t be easily migrated to a public cloud.
What are the limitations of private cloud?
Capital expense. While public clouds offer immediate access to cloud computing resources with no capital expenses, building a private cloud can incur costs for significant software and hardware, and may require substantial lead time.
Limits to scalability. As an organization and its computing requirements continue to grow, a private cloud will eventually reach the limits of its capacity. At this point, scaling up becomes more difficult, as it can be quite time-consuming to procure additional resources and add more capacity.
Management overhead. Organizations are responsible for managing capacity of a private cloud, adding additional overhead to internal IT teams.
What is the difference between private cloud and a traditional data center?
In many respects, a private cloud looks like a traditional data center located on a company’s premises and managed by an in-house IT team. However, there are several key differences between private clouds and on-premises data centers.
Virtualization. Private clouds are built with cloud technology, running virtual machines that maximize the use of hardware for greater efficiency.
Scalability. Private clouds can scale easily, enabling users to add services when needed.
Self-service. Private cloud computing enables users to access computing resources without help from IT.
Broader access. With a private cloud, users throughout the organization can access computing resources as needed.
Measurable usage. In a private cloud, IT teams can easily measure bandwidth, storage, and a number of user accounts to allocate resources effectively.
What is the difference between private cloud and public cloud?
A public cloud creates a pool of shared computing resources like servers, storage, and networking services that may reside anywhere in the world. Private clouds create pools of shared resources using hardware that is controlled solely by one organization. While public clouds offer increased scalability and allow organizations to pay only for the computing resources and cloud storage they consume, private clouds offer greater isolation and customization for more types of workloads.
What is the difference between private cloud and hybrid cloud?
A hybrid cloud is a combination of public cloud and private cloud services. A hybrid cloud allows organizations to choose the best cloud environment for individual applications and workloads. Organizations may choose to keep business-critical applications and sensitive data on a private cloud, while using a public cloud to access software as a service (SaaS) applications, to store non-critical business data, and to address bursts in workloads or spikes in demand. Orchestration and cloud management tools enable IT teams to move workloads seamlessly between the two environments to enhance performance, reduce cost, ensure regulatory compliance, and meet security requirements.
What is the difference between private cloud and multicloud?
A multicloud is a combination of two or more public cloud services. A hybrid multicloud includes a private cloud along with multiple public cloud deployments.
What are the types of private cloud?
On-premises. “On-prem” private clouds are deployed within an organization’s own data center. The organization must provision the hardware and hosting facilities (including space, electricity, and cooling) for the cloud platform, and in-house IT teams usually maintain the cloud architecture and operations. For this reason, on-prem private clouds are usually implemented by large enterprises that already have significant infrastructure and technical expertise.
Hosted. A hosted private cloud is operated from a data center outside of an organization’s premises. The organization provides the hardware and handles configuration and management, but the hosting operation is delivered by a service provider.
Managed. With a fully managed private cloud, the organization outsources management of cloud operations to a third-party provider. The hardware and hosting facilities may exist on the organization’s premises or in a data center operated by the managed service provider.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Private cloud is a cloud computing environment that serves the needs of a single organization. Private cloud solutions use the same virtualization and cloud management technologies that allow users to provision and configure computing resources on demand. However, the hardware for a private cloud is controlled and managed by one organization, rather than using hardware in data centers all over the world.
The public cloud refers to scalable, on-demand IT resources that are offered to businesses and individuals by third-party providers (cloud service providers, or CSPs), usually on a pay-as-you-go model. Public cloud offerings usually include IT infrastructure such as servers and virtual machines (VMs), applications, storage, databases, and more.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.