Yes, Netflix is considered software as a service (SaaS). It is a subscription-based streaming service that provides on-demand access to movies, television shows, and other media content.
An introduction to SaaS (software as a service)
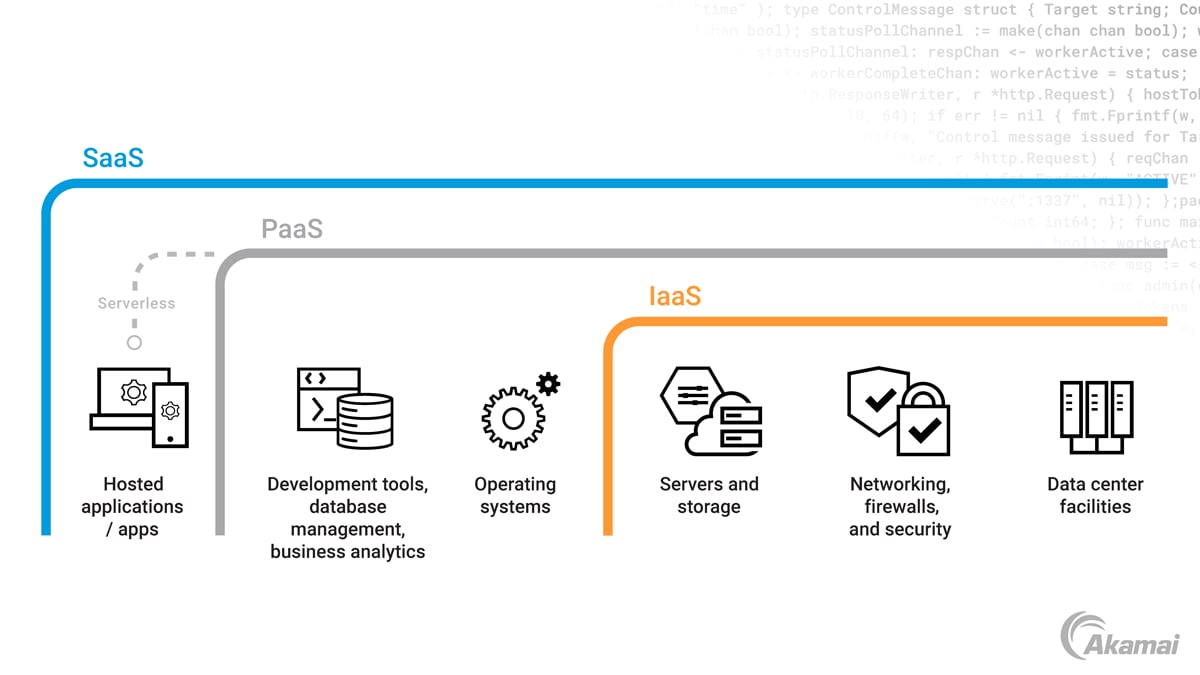
SaaS (software as a service) technology is one of the most visible ways in which cloud computing has transformed IT. With SaaS solutions, users can access software via the internet, on a subscription basis, rather than needing to install it on their own computers or servers.
This brief introduction to SaaS offers an overview of the technology as well as its benefits and challenges for businesses and their IT teams.
What is SaaS?
Software as a service, or SaaS, is a cloud computing solution that enables businesses and individuals to use software applications via a web browser or API, rather than installing software on a local hard drive or server. In the SaaS model, a third-party provider installs and manages the application on servers within a cloud platform, making the web-based software available to multiple customers. The cloud provider is responsible for maintaining, updating, and securing the software, freeing in-house IT teams from the routine tasks of managing software deployments.
How does SaaS work?
SaaS applications and services are usually offered from cloud platforms featuring a multi-tenant architecture. Through virtualization technology, cloud providers can run software from multiple virtual servers or virtual machines (VMs) that reside on a single physical server. This allows the cloud provider to offer services to multiple customers or tenants, who are all paying for access to a single instance of the software. Multi-tenant architecture enables cloud service providers to cost-effectively offer software services to more customers with less equipment and effort, significantly reducing costs. Multi-tenant technologies also allow providers to pool resources in ways that allow customers to scale up rapidly while making maintenance, updates, and troubleshooting more efficient.
What are the benefits of SaaS?
By allowing organizations and workers to access software over the internet rather than installing and running applications on their own systems, SaaS solutions provide a great number of benefits.
- Lower costs. Businesses can avoid the large upfront costs of purchasing and installing software systems on servers throughout the company.
- Remarkable scalability. Cloud-based services like SaaS are engineered to offer near limitless scalability, making it easy for businesses to respond to new opportunities and business requirements.
- Automatic updates. Rather than tasking IT teams with the important but tedious task of constantly updating and patching software solutions, organizations can rely on SaaS apps to make sure their software is always up to date.
- Efficient usage. Because SaaS solutions are offered on a pay-as-you-go basis, organizations can spend less on software costs and eliminate wasteful spending and overprovisioning.
- Mobile support. SaaS makes it easy to support a mobile workforce, allowing workers to access the applications they need via the internet, on any device, from any location, at any time.
- Access better software. SaaS solutions often allow businesses to access highly sophisticated software that they may not otherwise be able to afford to deploy and manage with existing IT resources.
- Higher uptime. SaaS companies invest heavily in security and offer industry-leading service level agreements (SLAs) for uptime and performance.
- Rapid deployment. Where it may take days, weeks, or months to procure and install traditional software on site, SaaS software can often be implemented within minutes or hours.
- Predictable costs. With SaaS, IT teams can count on predictable pricing month-to-month (barring an unplanned traffic spike), with no need to budget for periodic upgrades, hardware purchases to run software, or in-house IT staff to install and maintain applications.
What are the challenges of implementing
SaaS?
Loss of control. While IT teams have the freedom to choose or stick with a preferred version of on-premises software, SaaS providers typically determine which version of SaaS software they will roll out to all customers.
- Security concerns. Because data within SaaS solutions is not stored on premises, data privacy and data security are reliant on the security posture of the SaaS provider, which can vary from vendor to vendor.
- Slow performance. As SaaS solutions rely on internet connectivity, outages or slow internet connections may affect application performance.
- Vendor lock-in. Once a customer has adopted SaaS software and migrated data to the cloud, changing vendors or adopting a competing solution can be difficult.
- Shadow IT. Because SaaS products are so easy to provision, users often adopt them without the knowledge of an organization’s IT staff, creating security headaches and making the organization more vulnerable to threats.
Are SaaS solutions secure?
The fact that data in SaaS solutions is stored and managed by the third-party SaaS provider in an off-site location raises a variety of security concerns. There is an increased risk of unauthorized access to customer data and user account takeovers, since SaaS applications are exposed to the internet. Unpatched vulnerabilities and insecure APIs may be exploited by attackers. While many SaaS software vendors invest in advanced cloud security technology that surpasses the security controls and measures most companies can deploy on site, a lack of transparency may prevent businesses from truly knowing how secure their data is. Businesses can improve data security and privacy by encrypting data and implementing robust identity and access management controls.
What is SaaS vs. IaaS?
While SaaS solutions allow organizations to access applications as a service, IaaS (infrastructure as a service) offerings provide computing and data center resources as services. IaaS providers offer access to servers, storage, networking, and virtualization resources via an internet connection, enabling businesses to avoid the time and expense involved in installing and maintaining these systems on site.
What is SaaS vs. PaaS?
PaaS (platform as a service) solutions provide access to platforms that enable software development teams to build and run applications more securely and efficiently. Rather than purchasing, installing, and maintaining these resources on site, development teams and their organizations can access PaaS solutions via the internet to build, test, run, and scale applications faster and more cost-efficiently.
What are the types of SaaS solutions?
SaaS vendors offer a broad array of services. Some of the most common types of business applications and enterprise software available via SaaS platforms include:
- Customer relationship management (CRM) solutions
- Content management systems
- Enterprise resource planning (ERP) software
- Accounting and billing solutions
- Messaging and communications apps, including videoconferencing technology
- Human resources software
- Project management solutions
- Ecommerce software
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
SaaS applications, or software as a service applications, are part of a software delivery model that enables end users to access and use software that is hosted in the cloud by third-party providers, rather than software that is purchased and installed on local drives and servers. SaaS applications are usually available as a “pay as you go” or subscription-based service, enabling users and businesses to avoid the cost of purchasing, maintaining, and upgrading software solutions on site.
No, Amazon is not SaaS (software as a service). Amazon provides cloud-based services such as Amazon Web Services (AWS) and Amazon Elastic Compute Cloud (EC2), but these are not SaaS. SaaS is a type of cloud computing that provides access to software applications over the internet.
SaaS is a software distribution model that offers a lot of agility and cost-effectiveness for companies, making it an incredibly reliable option for numerous business models and industries. It’s also popular among companies due to its simplicity, user accessibility, security, and widespread connectivity.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.