Enterprise cloud computing allows businesses to access compute, storage, and networking resources from third-party providers via the internet, rather than provisioning and managing these resources with an in-house data center and network. Enterprise cloud computing enables businesses to use and pay only for the resources they need, achieving significant cost reduction and optimizing investment in technology.
Understanding the cloud
In the past two decades, the cloud has revolutionized IT and changed the way that businesses provision, use, and manage their technology. This brief overview offers a primer on the cloud and the advantages of cloud computing.
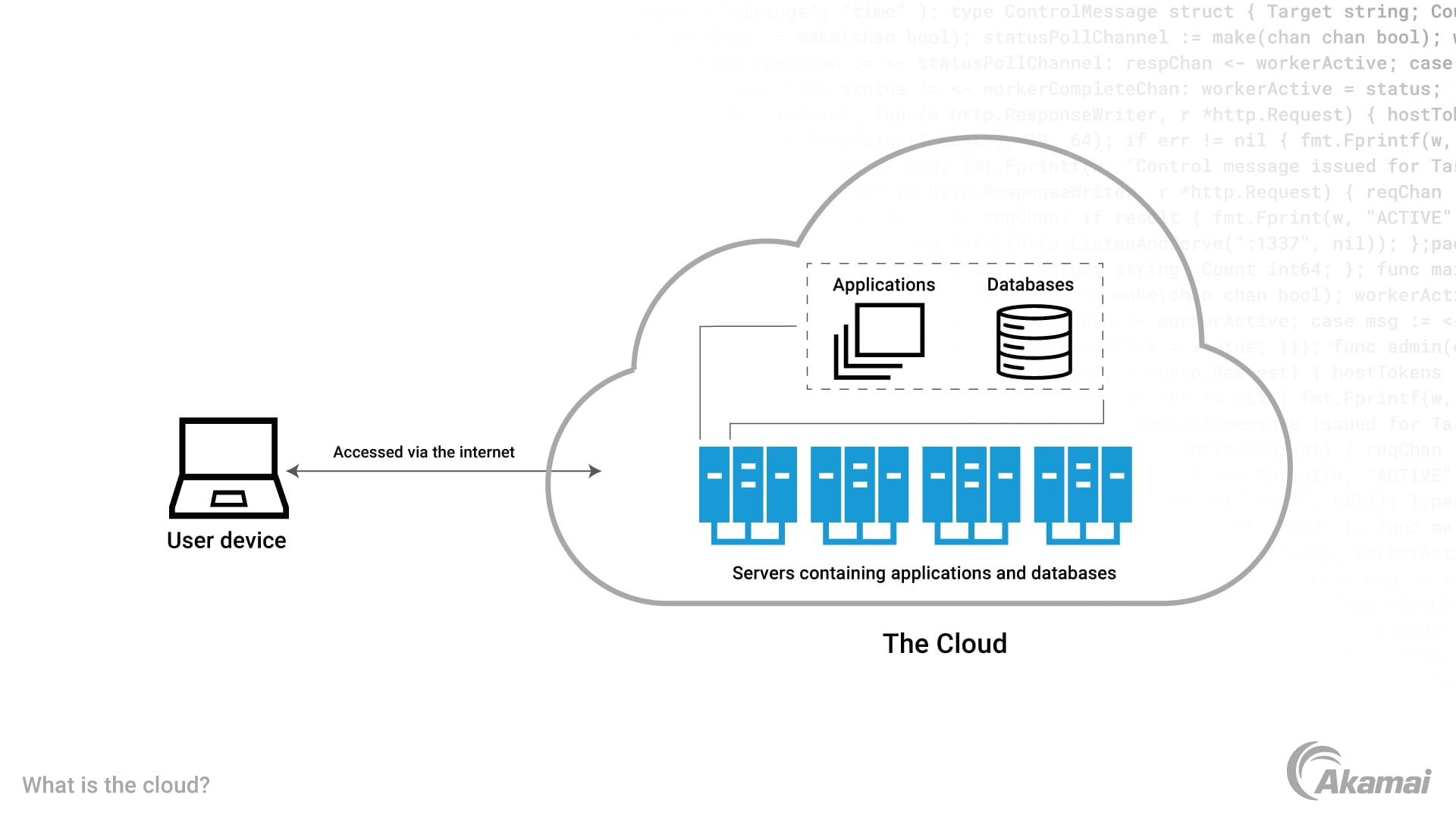
What is the cloud?
The cloud is made up of a vast network of computer servers located around the globe along with the data, content, applications, databases, and other computing resources that reside on these servers. The cloud enables businesses and consumers to access computing resources on demand via the internet, rather than installing their own physical servers, running their own software, and managing their own databases. The cloud allows users to access data, applications, and computing resources from anywhere in the world, rather than needing to be connected to a computer in an office.
How does cloud computing work?
Cloud computing is made possible by virtualization, a technology that allows multiple “virtual” computers (also known as virtual machines, or VMs) to run on a single server. Virtualization makes the use of physical hardware more efficient and allows one physical machine to serve many different needs and organizations. This reduces the cost of managing and accessing computing resources via the cloud while enabling greater redundancy to ensure reliable, faster access to data and computing resources.
What are the different types of cloud computing?
Cloud computing takes place in public, private, hybrid, or multicloud environments.
- A public cloud is operated by a cloud service provider (CSP) that provides cloud computing services to multiple organizations or customers. In a public cloud, there are typically multiple “tenants” renting space and consuming resources on virtual machines that reside on the same physical server. Accessed via the internet, public clouds enable businesses to achieve fast and flexible scalability, greater agility and elasticity, and significant cost savings.
- A private cloud is operated by one organization that has exclusive access to the resources on it, usually via a private network connection. Private clouds deliver the scalability, elasticity, and self-service features of the public cloud while providing higher levels of control and privacy.
- A hybrid cloud combines public and private clouds, which allows organizations to choose the best cloud for different workloads. For example, businesses may rely on the private cloud to run business-critical applications and use public cloud resources to scale up quickly to manage spikes in demand or bursts in workloads.
- A multicloud is the use of more than one cloud service from more than one cloud vendor. For instance, a business may use a cloud software solution like Salesforce and a cloud storage solution like AWS, creating a multicloud with two different vendors.
What are the different types of cloud service models?
Most cloud services fall into one of four models.
- Infrastructure as a service (IaaS) provides on-demand access to cloud infrastructure such as servers, storage, and networking. IaaS offerings are typically purchased from cloud providers on a pay-as-you-go basis, helping to reduce costs and to optimize IT budgets.
- Software as a service (SaaS) provides access for businesses and consumers to software applications in the cloud via a web browser. Rather than downloading and running an application from a hard drive on a specific computer, users can access SaaS applications on any device, from any location at any time, simply by connecting to the internet. SaaS providers handle all of the troubleshooting, maintenance, and frequent upgrades, ensuring that users are always working with software that has the latest features and capabilities. SaaS cloud applications are typically available for a subscription fee, which can save on the cost of provisioning, installing, and running software on site.
- Platform as a service (PaaS) provides organizations with an on-demand environment for developing, testing, delivering, and managing software applications. PaaS offerings are designed to help developers quickly create mobile or web apps without needing to worry about the infrastructure, servers, databases, storage, or network required for software development.
- Serverless computing helps developers build applications faster by taking the responsibility for managing infrastructure out of their hands. With serverless applications, a cloud service provider provisions and manages the infrastructure needed to run code, allowing developers to focus solely on the business logic and deliver more value for the organization.
What are the benefits of the cloud?
The cloud offers many advantages for businesses as they seek to accelerate innovation while reducing costs.
- Greater agility. With technologies and computing resources available in the cloud, businesses can innovate more easily, quickly spinning up resources like compute, storage, databases, machine learning, data lakes and analytics, and more. By making it possible to deploy technology in a matter of minutes, the cloud helps organizations move ideas to market faster than ever before.
- Improve elasticity. Rather than building up compute resources for anticipated spikes that may or may not occur, organizations can use the cloud to provision the exact amount of resources they need at any given moment, growing and shrinking capacity as business needs evolve.
- Reduced expense. The cloud lets businesses avoid capital investments in hardware, software, and the personnel needed to deploy and maintain them. By using and paying only for the cloud resources they need, businesses can also save money on operational costs.
- Easier disaster recovery. Storing data in the cloud eliminates single points of failure that may lead to disaster. When a disaster or outage occurs, businesses can quickly back up and restore data from cloud storage.
- Greater mobility. The cloud allows users to access data and applications from any device, anywhere, and at any time, ensuring that workers can stay productive no matter where they go.
- Stronger collaboration. Cloud computing makes it easier for users to communicate, share files, and edit documents collaboratively.
- Stronger security. Many cloud service providers deploy advanced security features that can deliver stronger security for data and resources in the cloud than what may exist in a company’s on-premises data center.
What are the limitations of the cloud?
For all its benefits, the cloud can have disadvantages, too.
- Occasional outages. Because access to the cloud requires an internet connection, computing resources may be unavailable to users when internet connectivity is spotty or when systems are offline. Outages can occur on the cloud side as well.
- Loss of control. When data, applications, and infrastructure is moved from an on-premises location to the cloud, businesses and their IT teams inevitably have less control over these computing resources.
- Security concerns. Many cloud vendors offer stronger security controls and technology than companies can deploy on site. Yet many vendors also operate with a shared responsibility security model that requires businesses to participate in the act of securing their data. When companies or IT teams don’t fully understand their responsibilities with each vendor under this model, security lapses can occur.
- Sluggish performance. Performance may be impacted when accessing cloud computing resources that are located in data centers that are too far away from end users. For this reason, many organizations are also adopting edge computing solutions that help to reduce latency.
What are typical cloud use cases?
Companies use the cloud for a wide range of purposes, but there are several common use cases that tend to dominate cloud activity.
- SaaS offerings. Software as a service technologies are one of the primary ways that businesses benefit from the cloud. These solutions enable users to access a broad array of tools and solutions, including CRM systems, marketing automation tools, and business productivity suites.
- Storage. Data storage solutions in the cloud enable businesses to store vast amounts of data and to manage file retention far more easily and cost-effectively than with on-premises drives and storage solutions.
- Big data analytics. The cloud has become an essential tool for businesses collecting, storing, and analyzing massive datasets.
- Testing and development. The cloud enables development teams to build environments easily, test them, and take them down quickly. Rather than waiting months to provision new environments, teams can now spin up environments in a matter of minutes.
- Virtual desktops. Companies can now support mobile and remote workforces with virtual desktops and desktop as a service (DaaS) solutions that enable workers to access the tools and resources they need from anywhere.
- Backups and disaster recovery. The cloud has made it easier, faster, and less costly to back up data and to recover quickly after an outage.
What is cloud security?
Security was once the primary obstacle for companies considering moving data and resources to the cloud. Today, however, most cloud service providers have invested in security measures that offer greater protection than on-premises data centers can manage. To strengthen security in the cloud, organizations can adopt several best practices and technologies to ensure that their data remains safe from theft, loss, and inaccessibility due to outages.
- Data encryption provides stronger protection for data at rest, in transit, and in use.
- User identity and access management solutions ensure that only authorized users can access data and resources in the cloud.
- Security and compliance monitoring technology provides early warning of potential breaches while ensuring that security measures are in compliance with regulatory frameworks.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Cloud optimization is the process of choosing and assigning cloud resources for workloads and applications to improve performance while optimizing cloud costs and eliminating waste.
Cloud waste is money spent unnecessarily on unused, underused, or ineffectively used services offered by public cloud service providers. Cloud waste and overspending are often the result of services that were once purchased for a specific purpose and never discontinued or taken down when the task was completed.
Cloud architecture is the way in which different technologies are combined to build a cloud, where businesses can access a pool of resources like compute power, data storage, and networking on demand.
A cloud platform is the operating system and hardware of a server that can host cloud applications. Cloud platforms enable businesses and individuals to purchase and use compute resources such as servers, databases, storage, networking, applications, and analytics without needing to purchase and install their own hardware and infrastructure.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.