ICMP and UDP floods are common because they are easy to execute and can be very effective in disrupting a network.
Understanding and preventing UDP flood DDoS attacks
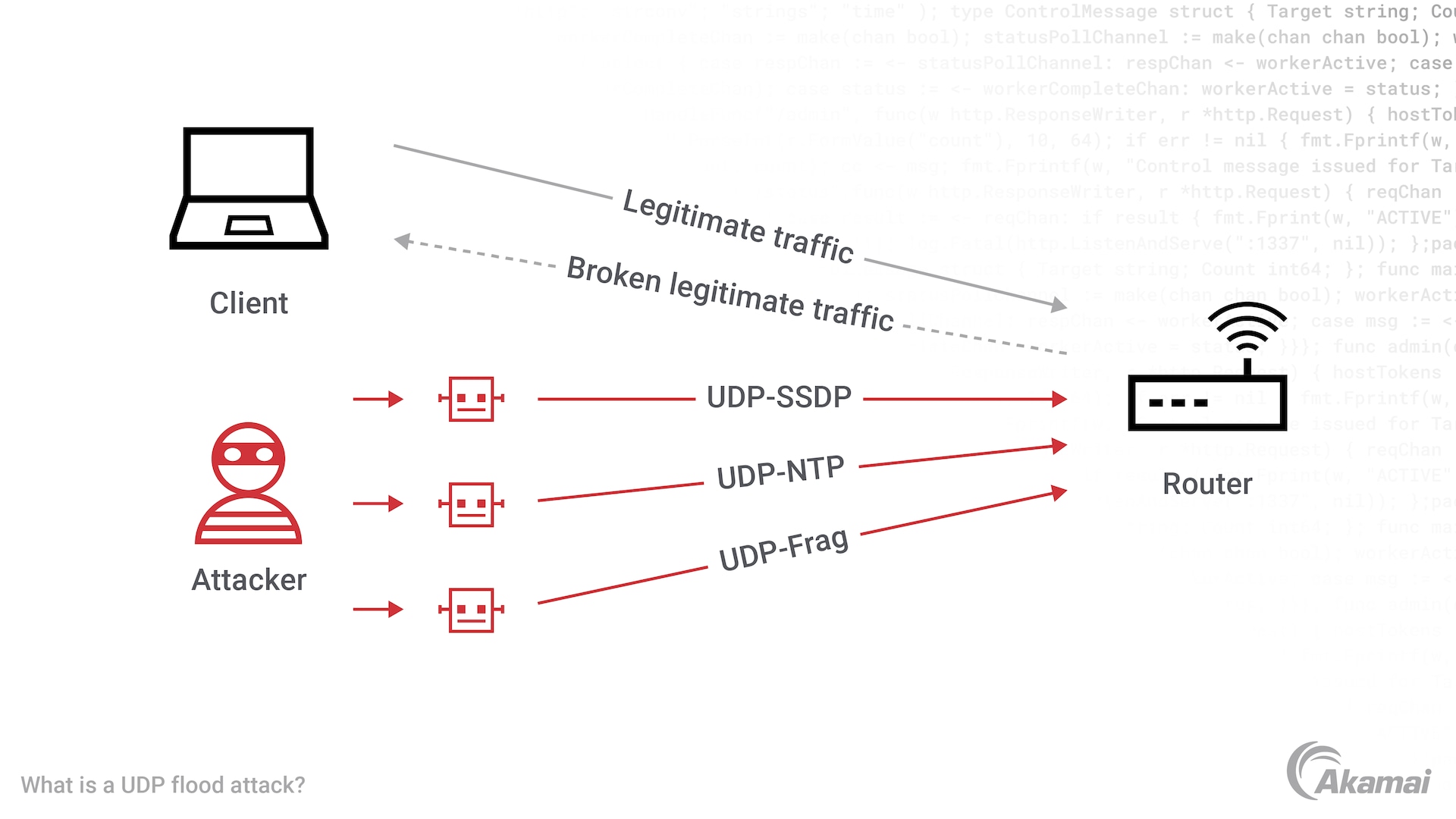
UDP flood is a type of denial-of-service (DoS) attack designed to render a system, server, bandwidth, or machine unavailable for legitimate users and requests. A sessionless protocol, UDP floods are highly effective and require few resources to execute. DoS or DDoS (distributed denial-of-service) attacks are often part of highly complex threats that combine multiple attack vectors (aka multi-vector), to target an organization’s IT environment. Unlike TCP DDoS attacks, where threat actors leverage TCP SYN packets, UDP packets can be fragmented and cause as much harm as a normal UDP flood attack.
DDoS protection, combining edge defenses, DNS resiliency, and cloud scrubbing technology designed to stop UDP floods and DDoS attacks before they can reach applications, data centers, and infrastructure. Hacker tools like Low Orbit Ion Cannon (LOIC) started to simplify the means in which attackers could leverage the UDP flood attack.
How a UDP flood works
The networking protocol User Datagram Protocol (UDP) enables computer applications to send messages, or datagrams, to other hosts via an IP address or network. When a UDP packet is received by a server, its operating system checks for related applications and, if none are found, informs the sender with a “destination unreachable” reply packet. Unlike TCP’s connection or session orientation, UDP is a connectionless protocol and the server uses the Internet Control Message Protocol (ICMP) response to serve notice that the original UDP packet cannot be delivered.
To initiate a UDP flood attack, attackers send large amounts of UDP traffic with spoofed IP addresses to random ports on a targeted system. Because the system must check the port specified in each incoming packet for a listening application and issue a response, the targeted server’s resource can quickly be exhausted, rendering it unavailable to normal traffic and legitimate users. Internet connections can easily become congested and saturated. When UDP packets are malformed with small header attack payloads, this increases the packets-per-second rates and can cause the hardware on internet network cards to fail.
Preventing UDP flood attacks can be a challenge. Operating systems may attempt to limit the response rate of the ICMP packets that are part of UDP responses. But this approach is indiscriminate and may filter out legitimate traffic as well. Mitigating any type of DDoS should be done furthest away from the data center or origin, where these attack tools are less effective. SIP and VOIP internet services rely on the UDP stack and are uniquely susceptible to these types of attacks. UDP flood attacks can be generated from botnets, but attackers leverage open UDP protocols that easily reflect and amplify attacks toward services like web, DNS, SSH, SCP, SSL, TLS, and other hosted internet resources.
Additional DDoS protection solutions
Along with Prolexic, Akamai offers additional solutions for DDoS protection.
App & API Protector
Akamai App & API Protector is holistic web application and API protection architecture and is designed to defend entire TCP web and API estates with an industry-leading focus on automation and simplicity. This solution brings together core technologies including API security, web application firewall, bot mitigation, and DDoS protection. App & API Protector defends against a broad range of threats, including volumetric DDoS attacks like UDP floods and ICMP floods, injection and API-based attacks, application-layer attacks like Slowloris, and protocol-based threats like TCP out-of-state attacks, SYN floods, or ACK floods that require legitimate users to complete the three-way handshake.
Prolexic
Akamai Prolexic stops UDP flood attacks with a zero-second SLA and the fastest, most effective defense at scale. Prolexic provides cloud-delivered mitigation across all ports and protocols to stop attacks in the cloud before they become business-impacting events. With Prolexic, network traffic is delivered to one of 20+ global high-capacity scrubbing centers, where we can stop attacks closer to the source to maximize performance for users and ensure network resiliency through cloud distribution. At each scrubbing center, the Akamai Security Operations Command Center (SOCC) uses proactive and/or custom mitigation controls to stop attacks instantly, returning clean traffic to the customer origin.
Edge DNS
Akamai Edge DNS is a cloud-based DNS solution that leverages Akamai Connected Cloud to provide access to thousands of DNS servers in more than 1,000 points of presence worldwide. With Edge DNS, organizations no longer need to rely just on two or three DNS servers, a common practice that leaves organizations vulnerable to data center outages and DDoS attacks. This Akamai solution can absorb the largest DDoS attacks while continuing to respond to legitimate user requests, improving DNS resiliency and responsiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
A UDP flood is a type of denial-of-service attack where malicious actors can spoof a source IP address and generate User Datagram Protocol (UDP) packets to a targeted server. When the server cannot find an application associated with the UDP packets, it answers with a “destination unreachable” packet. When the number of UDP packets received and answered becomes too much for the server to handle, the system becomes overwhelmed and cannot serve requests from legitimate clients and users.
As a common denial-of-service attack, a UDP flood can easily render a server or application unavailable to users. This can quickly result in a significant drop in productivity, loss of revenue, damage to reputation, and customer churn. UDP flood attacks are considered especially dangerous because there are no internal protections that can limit the rate of a UDP flood, so they can be executed by attackers with very few resources.
A UDP flood is more dangerous than a TCP flood because UDP is a connectionless protocol. This means that there is no need to establish a connection before sending data. UDP flood can easily overwhelm a server with spoofed packets.
Why customers choose Akamai
Akamai powers and protects life online. Leading companies worldwide choose Akamai to build, deliver, and secure their digital experiences — helping billions of people live, work, and play every day. Akamai Connected Cloud, a massively distributed edge and cloud platform, puts apps and experiences closer to users and keeps threats farther away.